
Back مارس 2 Arabic Марс 2 Bulgarian Mars 2 BS مارس ٢ CKB Mars 2 Czech Mars 2 Welsh Mars 2 German Άρης 2 (διαστημικό σκάφος) Greek Mars 2 Spanish مریخ ۲ Persian
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2014) |
 | |
| Mission type | Mars orbiter/lander |
|---|---|
| Operator | Soviet space program |
| COSPAR ID | 1971-045A 1971-045D |
| SATCAT no. | 5234 5739 |
| Mission duration | 1 year, 3 months and 3 days |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft type | 4M No. 171 |
| Manufacturer | OKB-1 |
| Launch mass | Total: 4,650 kg (10,250 lb) Orbiter: 3,440 kg (7,580 lb) Lander: 1,210 kg (2,670 lb)[1] |
| Landing mass | 358 kg (789 lb) |
| Dry mass | 2,265 kg (4,993 lb) |
| Dimensions | 4.1 × 2.0 × 5.9 m (13.5 × 6.6 × 19.4 ft) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 19 May 1971, 16:22:44 UTC |
| Rocket | Proton-K/D |
| Launch site | Baikonur 81/24 |
| Contractor | Khrunichev |
| End of mission | |
| Disposal | Decommissioned |
| Declared | August 22, 1972 |
| Last contact | July 1972[2] |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Areocentric[3] |
| Periareion altitude | 1,380 km (860 mi) |
| Apoareion altitude | 24,940 km (15,500 mi) |
| Inclination | 48.9° |
| Period | 18 hours |
| Mars orbiter | |
| Orbital insertion | 27 November 1971 |
| Orbits | 362 |
| Mars impact (failed landing) | |
| Impact date | 27 November 1971 |
| Impact site | 45°S 47°E / 45°S 47°E |
 Mars 2 stamp | |
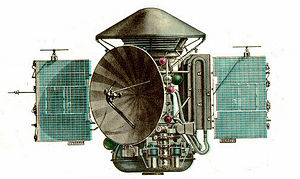
The Mars 2 was an uncrewed space probe of the Mars program, a series of uncrewed Mars landers and orbiters launched by the Soviet Union beginning 19 May 1971.
The Mars 2 and Mars 3 missions consisted of identical spacecraft, each with an orbiter and an attached lander. The orbiter is identical to the Venera 9 bus. The type of bus/orbiter is the 4MV. They were launched by a Proton-K heavy launch vehicle with a Blok D upper stage. The lander of Mars 2 became the first human-made object to reach the surface of Mars, although the landing system failed and the lander was lost.
- ^ "NASA - NSSDCA - Spacecraft - Details".
- ^ See Mars 3 article in https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/resources/1060/beyond-earth-a-chronicle-of-deep-space-exploration/
- ^ Mark Wade. "Mars M-71". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Retrieved 27 May 2024.