
Back أذن وسطى Arabic Srednje uho BS Orella mitjana Catalan Střední ucho Czech Вăта хăлха CV Y glust ganol Welsh Mellemøre Danish Mittelohr German Μεσαίο αυτί Greek Oído medio Spanish
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2023) |
| Middle ear | |
|---|---|
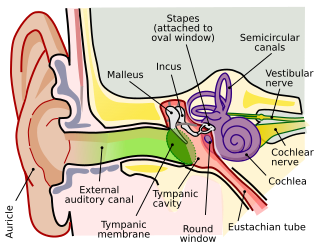 A diagram of the anatomy of the human ear: Brown is outer ear.
Red is middle ear.
Purple is inner ear. | |
| Details | |
| Nerve | Glossopharyngeal nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | auris media |
| MeSH | D004432 |
| TA98 | A15.3.02.001 |
| TA2 | 6877 |
| FMA | 56513 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
 |
| This article is one of a series documenting the anatomy of the |
| Human ear |
|---|
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear).
The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes), which transfer the vibrations of the eardrum into waves in the fluid and membranes of the inner ear. The hollow space of the middle ear is also known as the tympanic cavity and is surrounded by the tympanic part of the temporal bone. The auditory tube (also known as the Eustachian tube or the pharyngotympanic tube) joins the tympanic cavity with the nasal cavity (nasopharynx), allowing pressure to equalize between the middle ear and throat.
The primary function of the middle ear is to efficiently transfer acoustic energy from compression waves in air to fluid–membrane waves within the cochlea.