
Back Moab Afrikaans مملكة موآب Arabic مؤاب ARZ Moav Azerbaijani موأب AZB Моав Bulgarian মোয়াব Bengali/Bangla Moab (rouantelezh) Breton Regne de Moab Catalan Moáb Czech
Kingdom of Moab 𐤌𐤀𐤁 | |
|---|---|
| c. 13th century BCE – c. 400 BCE | |
 | |
| Status | Monarchy |
| Capital | Dibon |
| Common languages | Moabite |
| Religion | Canaanite religion |
| History | |
• Established | c. 13th century BCE |
• Collapsed | c. 400 BCE |
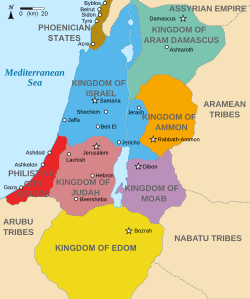
| Today part of | Jordan |
Moab[a] (/ˈmoʊæb/) was an ancient Levantine kingdom whose territory is today located in southern Jordan. The land is mountainous and lies alongside much of the eastern shore of the Dead Sea. The existence of the Kingdom of Moab is attested to by numerous archaeological findings, most notably the Mesha Stele, which describes the Moabite victory over an unnamed son of King Omri of Israel, an episode also noted in 2 Kings 3. The Moabite capital was Dibon. According to the Hebrew Bible, Moab was often in conflict with its Israelite neighbours to the west.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).