
Back نيبيفولول Arabic Nebivolol BS Nebivolol German Νεμπιβολόλη Greek Nebivolol Spanish نبیوولول Persian Nebivololi Finnish Nébivolol French Nebivolol Hungarian Nebivololo Italian
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nebilet, Bystolic, others |
| Other names | Narbivolol, Nebivolol, Nebivololum[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608029 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 98% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2D6-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 12-19 hours[2][3][4] |
| Excretion | Kidney and fecal |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
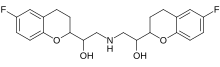
| Formula | C22H25F2NO4 |
| Molar mass | 405.442 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |

Nebivolol is a beta blocker used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure.[5] As with other β-blockers, it is generally a less preferred treatment for high blood pressure.[6] It may be used by itself or with other blood pressure medication.[6] It is taken by mouth.[6]
Common side effects include dizziness, feeling tired, nausea, and headaches.[6] Serious side effects may include heart failure and bronchospasm.[6] Its use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended.[5][7] It works by blocking β1-adrenergic receptors in the heart and dilating blood vessels.[6][8]
Nebivolol was patented in 1983 and came into medical use in 1997.[9] It is available as a generic medication in the United Kingdom.[5] In 2022, it was the 173rd most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3 million prescriptions.[10][11]
- ^ "Nebivolol". go.drugbank.com. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
- ^ "Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs Nebivolol - ALLERGAN" (PDF). accessdata.fda.gov. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
- ^ Giles TD, Cockcroft JR, Pitt B, Jakate A, Wright HM (September 2017). "Rationale for nebivolol/valsartan combination for hypertension: review of preclinical and clinical data". Journal of Hypertension. 35 (9): 1758–1767. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000001412. PMC 5548499. PMID 28509722.
- ^ "DrugBank Nebivolol". go.drugbank.com. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
- ^ a b c British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 154. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ a b c d e f "Nebivolol Hydrochloride Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "Nebivolol Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ de Boer RA, Voors AA, van Veldhuisen DJ (July 2007). "Nebivolol: third-generation beta-blockade". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 8 (10): 1539–1550. doi:10.1517/14656566.8.10.1539. PMID 17661735. S2CID 24186687.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 462. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Nebivolol Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.