
Back قشرة جديدة Arabic Neocórtex AST Neocòrtex Catalan Neokortex Danish Neocortex German Neocórtex Spanish Neokortex Basque نئوکورتکس Persian Néocortex French Neocoirtéis Irish
| Neocortex | |
|---|---|
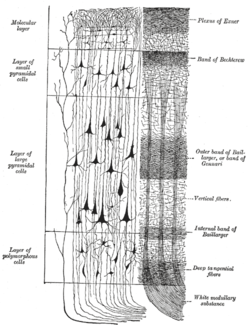 A representative column of neocortex. Cell body layers are labeled on the left, and fiber layers are labeled on the right. | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D019579 |
| NeuroNames | 2314 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_2547 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.304 A14.1.09.307 |
| TA2 | 5532 |
| FMA | 62429 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands,[1] spatial reasoning and language.[2] The neocortex is further subdivided into the true isocortex and the proisocortex.[3]
In the human brain, the cerebral cortex consists of the larger neocortex and the smaller allocortex, respectively taking up 90% and 10%.[4] The neocortex is made up of six layers, labelled from the outermost inwards, I to VI.
- ^ Lodato S, Arlotta P (2015-11-13). "Generating neuronal diversity in the mammalian cerebral cortex". Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 31 (1): 699–720. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100814-125353. PMC 4778709. PMID 26359774.
The neocortex is the part of the brain responsible for execution of higher-order brain functions, including cognition, sensory perception, and sophisticated motor control.
- ^ Lui JH, Hansen DV, Kriegstein AR (July 2011). "Development and evolution of the human neocortex". Cell. 146 (1): 18–36. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.030. PMC 3610574. PMID 21729779.
- ^ "BrainInfo". braininfo.rprc.washington.edu.
- ^ Saladin, K (2012). Anatomy & physiology : the unity of form and function (6th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. p. 417. ISBN 9780073378251.