| North Downs Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
| Overview | |||
| Status | Operational | ||
| Owner | Network Rail | ||
| Locale | Berkshire, Hampshire, Surrey, Sussex | ||
| Termini | |||
| Service | |||
| Type | Suburban rail, Heavy rail | ||
| System | National Rail | ||
| Operator(s) | Great Western Railway South Western Railway Southern | ||
| Rolling stock | Class 165, Class 166, Class 450, Class 458, Class 377 | ||
| History | |||
| Opened | 1849 | ||
| Technical | |||
| Line length | 41 mi 40 ch (66.8 km) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification | 3rd rail, 750 V DC (Reading–Wokingham; Aldershot South Junction–Guildford; Reigate–Redhill) | ||
| Operating speed | 70 mph (110 km/h) (maximum) | ||
| |||
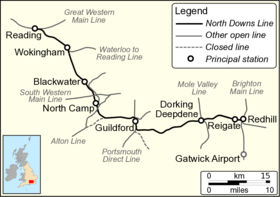
The North Downs Line is a railway line in South East England. It runs for 41 miles 40 chains (66.8 km) from Reading in Berkshire to Redhill in Surrey. It is named after the North Downs, a range of chalk hills that runs parallel to the eastern part of the route. The name was introduced in 1989 by Network SouthEast, the then operator. The North Downs Line serves the settlements in the Blackwater Valley as well as the towns of Guildford, Dorking and Reigate. It acts as an orbital route around the south and southwest of London and has direct connections to the Great Western Main Line at Reading, the Waterloo-Reading line at Wokingham, the Alton line at Ash, the Portsmouth Direct Line at Guildford and the Brighton Main Line at Redhill.
Three different operators run passenger services on the North Downs Line. GWR runs semi-fast and stopping services along the entire length of the line from Reading to Redhill, the majority of which continue along the Brighton Main Line to Gatwick Airport. Southern trains between Reigate and London Victoria use a 1 mi 67 ch (3.0 km) section west of Redhill. South Western Railway services between the capital and Reading use the line west of Wokingham and the same company operates between Guildford and Ash en route to Aldershot.
The majority of the North Downs Line was constructed by the independent Reading, Reigate and Guildford Railway company (RG&RR), although the section between Guildford and Ash Junction was built by the London and South Western Railway. The line opened in 1849 and services were run from the outset by the South Eastern Railway, which took over the RG&RR in 1852. Three sections of the line were electrified by the Southern Railway in the 1930s, although around 29 miles (47 km) remains unelectrified. In the early 21st century, infrastructure works to increase the capacity of the line were undertaken, including the provision of new platforms at Reading and Redhill.