
Back Noordelike Halfrond Afrikaans Norðerne healftrendel ANG نصف الأرض الشمالي Arabic ܩܫܬܐ ܓܪܒܝܝܬܐ ܕܐܪܥܐ ARC نص شمالي د لأرض ARY Hemisferiu norte AST Şimal yarımkürəsi Azerbaijani قوزئی یاریم کوره AZB Amihanan na Emisperyo BCL Паўночнае паўшар’е Byelorussian
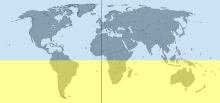
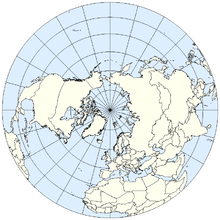
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar System as Earth's North Pole.[1]
Due to Earth's axial tilt of 23.439281°, there is a seasonal variation in the lengths of the day and night. There is also a seasonal variation in temperatures, which lags the variation in day and night. Conventionally, winter in the Northern Hemisphere is taken as the period from the December solstice (typically December 21 UTC) to the March equinox (typically March 20 UTC), while summer is taken as the period from the June solstice through to the September equinox (typically on 23 September UTC). The dates vary each year due to the difference between the calendar year and the astronomical year. Within the Northern Hemisphere, oceanic currents can change the weather patterns that affect many factors within the north coast. Such events include El Niño–Southern Oscillation.
Trade winds blow from east to west just above the equator. The winds pull surface water with them, creating currents, which flow westward due to the Coriolis effect. The currents then bend to the right, heading north. At about 30 degrees north latitude, a different set of winds, the westerlies, push the currents back to the east, producing a closed clockwise loop.[2]
Its surface is 60.7% water, compared with 80.9% water in the case of the Southern Hemisphere, and it contains 67.3% of Earth's land.[3] The continents of North America and mainland Eurasia are located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere, together with about two-thirds of Africa and a small part of South America.
- ^ Archinal, Brent A.; A'Hearn, Michael F.; Bowell, Edward G.; Conrad, Albert R.; Consolmagno, Guy J.; et al. (2010). "Report of the IAU Working Group on Cartographic Coordinates and Rotational Elements: 2009" (PDF). Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy. 109 (2): 101–135. Bibcode:2011CeMDA.109..101A. doi:10.1007/s10569-010-9320-4. S2CID 189842666. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2018-09-26.
- ^ "Ocean Currents". National Geographic Society. 2019-07-01. Archived from the original on 2021-11-20. Retrieved 2020-10-16.
- ^ Life on Earth: A – G.. 1. ABC-CLIO. 2002. p. 528. ISBN 9781576072868. Archived from the original on 22 January 2023. Retrieved 8 September 2016.