Back Норвегиа Abkhazian Norwègia ACE Норвегие ADY Noorweë Afrikaans Norwegen ALS ኖርዌይ Amharic Norway AMI Noruega AN Norþweg ANG Nọwè ANN
Kingdom of Norway Kongeriket Norge (Bokmål) Kongeriket Noreg (Nynorsk) Other official names
| |
|---|---|
| Anthem: Ja, vi elsker dette landet (English: "Yes, we love this country") | |
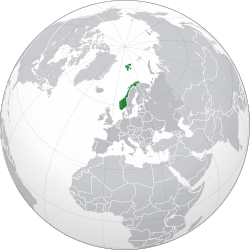
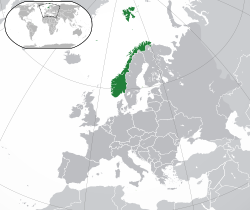
Location of the Kingdom of Norway (green) in Europe (green and dark grey) | |
| Capital and largest city | Oslo 59°56′N 10°41′E / 59.933°N 10.683°E |
| Official languages | |
| Recognised national languages | |
| Ethnic groups |
|
| Religion |
|
| Demonym(s) | Norwegian |
| Government | Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Harald V |
| Jonas Gahr Støre | |
| Masud Gharahkhani | |
| Toril Marie Øie | |
| Legislature | Storting |
| History | |
| 872 | |
• Old Kingdom of Norway (Peak extent) | 1263 |
| 1397 | |
| 1524 | |
| 25 February 1814 | |
| 17 May 1814 | |
| 4 November 1814 | |
| 7 June 1905 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 385,207 km2 (148,729 sq mi)[13] (61stb) |
• Water (%) | 5.32 (2015)[12] |
| Population | |
• 2024 estimate | |
• Density | 14.4/km2 (37.3/sq mi) (227th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2024 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2020) | low inequality |
| HDI (2022) | very high (2nd) |
| Currency | Norwegian krone (NOK) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Date format | dd.mm.yyyy |
| Drives on | right |
| Calling code | +47 |
| ISO 3166 code | NO |
| Internet TLD | .nod |
| |
Norway (Bokmål: Norge, Nynorsk: Noreg), officially the Kingdom of Norway,[a] is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula with a population of 5.5 million as of 2024.[19] The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of Norway.[note 5] Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency, and not a part of the Kingdom; Norway also claims the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo.
Norway has a total area of 385,207 square kilometres (148,729 sq mi).[13] The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden, and is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast. Norway has an extensive coastline facing the Skagerrak strait, the North Atlantic Ocean, and the Barents Sea. Harald V of the House of Glücksburg is the current King of Norway. Jonas Gahr Støre has been Prime Minister of Norway since 2021. As a unitary state with a constitutional monarchy, Norway divides state power between the parliament, the cabinet, and the supreme court, as determined by the 1814 constitution.
The unified kingdom of Norway was established in 872 as a merger of petty kingdoms and has existed continuously for 1,151–1,152 years. From 1537 to 1814, Norway was part of Denmark–Norway, and, from 1814 to 1905, it was in a personal union with Sweden. Norway was neutral during the First World War, and in the Second World War until April 1940 when it was invaded and occupied by Nazi Germany until the end of the war.
Norway has both administrative and political subdivisions on two levels: counties and municipalities. The Sámi people have a certain amount of self-determination and influence over traditional territories through the Sámi Parliament and the Finnmark Act. Norway maintains close ties with the European Union and the United States. Norway is a founding member of the United Nations, NATO, the European Free Trade Association, the Council of Europe, the Antarctic Treaty, and the Nordic Council; a member of the European Economic Area, the WTO, and the OECD; and a part of the Schengen Area. The Norwegian dialects share mutual intelligibility with Danish and Swedish.
Norway maintains the Nordic welfare model with universal health care and a comprehensive social security system, and its values are rooted in egalitarian ideals.[21] The Norwegian state has large ownership positions in key industrial sectors, having extensive reserves of petroleum, natural gas, minerals, lumber, seafood, and fresh water. The petroleum industry accounts for around a quarter of the country's gross domestic product (GDP).[22] On a per-capita basis, Norway is the world's largest producer of oil and natural gas outside of the Middle East.[23][24] The country has the fourth- and eighth-highest per-capita income in the world on the World Bank's and IMF's list, respectively.[25] It has the world's largest sovereign wealth fund, with a value of US$1.3 trillion.[26][27]
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
LanguageCouncilSamiwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Minoritetsspråk". Språkrådet. Archived from the original on 15 January 2018. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- ^ "Immigrants and their children as of 1 January 2020". Statistics Norway. 9 March 2020. Archived from the original on 3 January 2021. Retrieved 26 December 2020.
- ^ "Immigrants and Norwegian-born to immigrant parents". Statistics Norway. 9 March 2021. Archived from the original on 10 April 2021. Retrieved 30 March 2021.
- ^ "Samer". Regjeringen.no. Fornyings- administrasjons- og kirkedepartementet. 16 June 2006. Archived from the original on 9 January 2018. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- ^ inkluderingsdepartementet, Arbeids- og (16 June 2006). "Nasjonale minoriteter". Regjeringen.no. Archived from the original on 5 December 2017. Retrieved 8 January 2018.
- ^ "05183: Immigrants and Norwegian-born to immigrant parents, by sex and country background 1970 – 2021-PX-Web SSB". SSB.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Church of Norway Archived 16 June 2021 at the Wayback Machine Statistics Norway 15 June 2021
- ^ Members of religious and life stance communities outside the Church of Norway, by religion/life stance. Archived 6 December 2022 at the Wayback Machine Statistics Norway 27 September 2021
- ^ "The Constitution of Norway, Article 16 (English translation, published by the Norwegian Parliament)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 September 2015.
- ^ "The Re-establishing of a Norwegian State". regjeringen.no. 5 July 2020. Archived from the original on 18 April 2017. Retrieved 17 April 2017.
- ^ "Surface water and surface water change". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Archived from the original on 24 March 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2020.
- ^ a b c "Arealstatistics for Norway 2019". Kartverket, mapping directory for Norway. 20 December 2019. Archived from the original on 8 June 2019. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- ^ "Population, 2024-01-01". Statistics Norway. 1 January 2024. Archived from the original on 4 May 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2024.
- ^ a b c d "World Economic Outlook Database, October 2024 Edition. (Norway)". www.imf.org. International Monetary Fund. 22 October 2024. Retrieved 27 October 2024.
- ^ "Gini coefficient of equivalised disposable income – EU-SILC survey". ec.europa.eu. Eurostat. Archived from the original on 9 October 2020. Retrieved 22 June 2022.
- ^ "Human Development Report 2023/2024" (PDF). United Nations Development Programme. 13 March 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 March 2024. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ "Norway". CIA World fact. 26 October 2021. Archived from the original on 11 January 2021. Retrieved 12 February 2021.
- ^ "Norway Population 2024 (Live)". worldpopulationreview.com. Retrieved 9 August 2024.
- ^ National Research Council (U.S.). Polar Research Board (1986). Antarctic treaty system: an assessment. National Academies Press. ISBN 978-0309036405. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ^ "Norwegian Society / Living in Norway". Study in Norway. Archived from the original on 21 March 2018. Retrieved 21 March 2018.
- ^ "Statistics Norway raises '07 GDP outlook, cuts '08". Reuters. 6 September 2007. Archived from the original on 22 September 2020. Retrieved 8 March 2009.
- ^ "Country Comparison :: Crude oil – production". CIA – The World Factbook. Archived from the original on 7 March 2017. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- ^ "Country Comparison :: Natural gas – production". CIA – The World Factbook. Archived from the original on 15 March 2016. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- ^ "The World's Richest Countries". forbes.com. Archived from the original on 31 January 2018. Retrieved 12 December 2014.
- ^ Holter, Mikael (27 June 2017). "The World's Biggest Wealth Fund Hits $1 Trillion". Bloomberg L.P. Archived from the original on 19 September 2017. Retrieved 19 September 2017.
- ^ Meredith, Sam (31 January 2023). "Norway's gigantic sovereign wealth fund loses a record $164 billion, citing 'very unusual' year". CNBC. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 26 April 2023.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).