
Back تصحيح البصر Arabic Оптометрия Bulgarian Optometria Catalan Optometrie Czech Optometrie German Optometría Spanish بیناییسنجی Persian Optometria Finnish Optométrie French Radharcmheastóireacht Irish
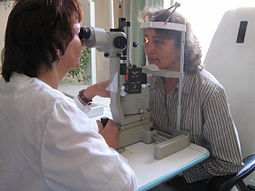 Eye examination with the aid of a slit lamp | |
| System | Eye |
|---|---|
| Significant diseases | Blurred vision, cataract, macular degeneration, glaucoma, refractive error, retinal disorders, diabetic retinopathy |
| Significant tests | Visual field test, ophthalmoscopy |
| Occupation | |
|---|---|
| Names | Doctor of Optometry, Optometrist |
Occupation type | Health Profession |
Activity sectors | Healthcare |
| Description | |
| Competencies | refractive error, ocular disease, medical therapeutics, binocular vision, sports vision, vision therapy, contact lenses |
Education required | Doctor of Optometry / Master of Optometry / Bachelor of Optometry |
Fields of employment | Hospital, Clinic, Laboratory |
Optometry is a specialized health care profession that involves examining the eyes and related structures for defects or abnormalities. Optometrists are health care professionals who typically provide comprehensive eye care.
In the United States of America and Canada, optometrists are those that hold a Doctor of Optometry degree. They are trained and licensed to practice medicine for eye related conditions, in addition to providing refractive (optical) eye care. Within their scope of practice, optometrists are considered physicians and bill medical insurance(s) (example: Medicare) accordingly.
In the United Kingdom, optometrists may also provide some medical care (e.g. prescribe some medications) for eye-related conditions in addition to providing refractive care. The Doctor of Optometry degree is rarer in the UK.
Many optometrists participate in academic research for eye-related conditions and diseases. Optometrists receive training in refraction and monitoring of common uncomplicated eye conditions. They are not trained in any forms of surgery or laser procedures. Ophthalmologists are medical doctors and surgeons who typically hold a four-year college degree, a four-year medical degree, and at least four years of residency training after medical school.