
Back اتجاهات دورية Arabic Dövri qanun Azerbaijani Перыядычныя ўласцівасці атамаў Byelorussian মৌলের পর্যায়বৃত্ত ধর্ম Bengali/Bangla Periodický zákon Czech Периодла саккун CV Perioodilisusseadus Estonian روندهای تناوبی Persian Tendances périodiques French આવર્ત નિયમ Gujarati
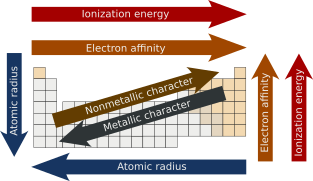
In chemistry, periodic trends are specific patterns present in the periodic table that illustrate different aspects of certain elements when grouped by period and/or group. They were discovered by the Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1863. Major periodic trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, valency and metallic character. These trends exist because of the similar electron configurations of the elements within their respective groups or periods; they reflect the periodic nature of the elements. These trends give a qualitative assessment of the properties of each element.[1][2]
- ^ The Periodic Table I. Structure and Bonding. Vol. 181. 2019. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-40025-5. ISBN 978-3-030-40024-8. S2CID 211038510.
- ^ Schrobilgen, Gary J. (2019), Mingos, D. Michael P. (ed.), "Chemistry at the Edge of the Periodic Table: The Importance of Periodic Trends on the Discovery of the Noble Gases and the Development of Noble-Gas Chemistry", The Periodic Table I: Historical Development and Essential Features, Structure and Bonding, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp. 157–196, doi:10.1007/430_2019_49, ISBN 978-3-030-40025-5, S2CID 213379908, retrieved 2022-07-02