Back فينيل ألانين Arabic فينيل ألانين ARZ Fenilalanin Azerbaijani فنیلآلانین AZB Фенілаланін Byelorussian Фенилаланин Bulgarian Fenilalanin BS Fenilalanina Catalan Fenylalanin Czech Fenylalanin Danish
 Skeletal formula of L-phenylalanine
| |||
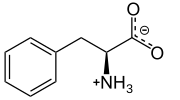 L-Phenylalanine at physiological pH
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | US: /ˌfɛnəlˈæləniːn/; UK: /ˌfiːnaɪl-/ | ||
| IUPAC name
Phenylalanine
| |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
(S)-2-Amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChEMBL |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.517 | ||
| |||
| KEGG |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C9H11NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 165.192 g·mol−1 | ||
| 9.97 g/L at 0 °C 14.11 g/L at 25 °C | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 1.83 (carboxyl), 9.13 (amino)[2] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Phenylalanine (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F)[3] is an essential α-amino acid with the formula C
9H
11NO
2. It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins coded for by DNA. Phenylalanine is a precursor for tyrosine, the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), and the biological pigment melanin. It is encoded by the messenger RNA codons UUU and UUC.
Phenylalanine is found naturally in the milk of mammals. It is used in the manufacture of food and drink products and sold as a nutritional supplement as it is a direct precursor to the neuromodulator phenethylamine. As an essential amino acid, phenylalanine is not synthesized de novo in humans and other animals, who must ingest phenylalanine or phenylalanine-containing proteins.
The one-letter symbol F was assigned to phenylalanine for its phonetic similarity.[4]
- ^ a b Ihlefeldt FS, Pettersen FB, von Bonin A, Zawadzka M, Görbitz PC (2014). "The Polymorphs of L-Phenylalanine". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53 (49): 13600–13604. doi:10.1002/anie.201406886. PMID 25336255.
- ^ Dawson RM, et al. (1959). Data for Biochemical Research. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- ^ "Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides". IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. 1983. Archived from the original on 9 October 2008. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ "IUPAC-IUB Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature A One-Letter Notation for Amino Acid Sequences". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 243 (13): 3557–3559. 10 July 1968. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)34176-6.