
Back Polske stammer Danish Πολωνικές φυλές Greek ポーランド族 Japanese Plemiona polskie Polish Польские племена Russian Polonya kabileleri Turkish Польські племена Ukrainian
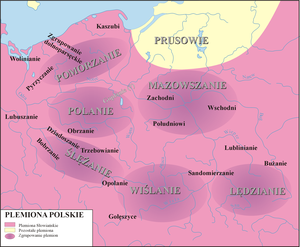
"Polish tribes" is a term used sometimes to describe the tribes of West Slavic Lechites that lived from around the mid-6th century in the territories that became Polish with the creation of the Polish state by the Piast dynasty. The territory on which they lived became a part of the first Polish state created by duke Mieszko I and expanded at the end of the 10th century, enlarged further by conquests of king Bolesław I at the beginning of the 11th century.
In about 850 AD a list of peoples was written down by the Bavarian Geographer. Absent on the list are Lechitic-speaking Polans, Pomeranians and Masovians, who became known later and were written about by Nestor the Chronicler in his Primary Chronicle (11th/12th century).
The most important tribes who were conquered by Polans were the Masovians, Vistulans, Silesians and Pomeranians.[1] These five tribes "shared fundamentally common culture and language and were considerably more closely related to one another than were the Germanic tribes."[2]
- ^ Raymond Breton, National Survival in Dependent Societies: Social Change in Canada and Poland, McGill-Queen's Press - MQUP, 1990, p. 106,ISBN 0-88629-127-5 Google Books
- ^ John Blacking, Anna Czekanowska, Polish Folk Music: Slavonic Heritage - Polish Tradition - Contemporary Trends, Cambridge University Press, 2006, p. 3, ISBN 0-521-02797-7 Google Books
