
Back تثليث مضلع Arabic Triangulació d'un polígon Catalan Нумайкĕтеслĕх триангуляцийĕн тĕллевчĕкĕ CV Polygon-Triangulation German Triangulación de un polígono Spanish مثلثبندی چندضلعیها Persian Triangulation d'un polygone French 多角形の三角形分割 Japanese Triangularea unui poligon Romanian Задача о триангуляции многоугольника Russian
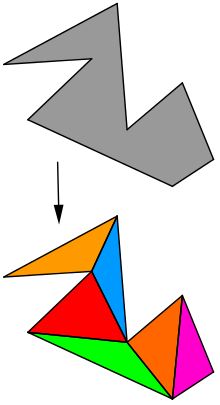
In computational geometry, polygon triangulation is the partition of a polygonal area (simple polygon) P into a set of triangles,[1] i.e., finding a set of triangles with pairwise non-intersecting interiors whose union is P.
Triangulations may be viewed as special cases of planar straight-line graphs. When there are no holes or added points, triangulations form maximal outerplanar graphs.
- ^ Mark de Berg, Marc van Kreveld, Mark Overmars, and Otfried Schwarzkopf (2000), "3: Polygon Triangulation", Computational Geometry (2nd ed.), Springer-Verlag, pp. 45–61, ISBN 3-540-65620-0
{{citation}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)