
Back فرط ضغط الدم البابي Arabic Portal hipertenziya Azerbaijani পোর্টাল হাইপারটেনশন Bengali/Bangla Hipertensió portal Catalan Portální hypertenze Czech Portale Hypertension German Hipertensión portal Spanish پرفشاری ورید باب Persian Hypertension portale French Hipertensión portal Galician
| Portal hypertension | |
|---|---|
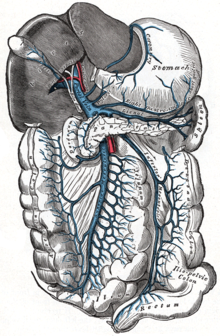 | |
| The portal vein and its tributaries | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
| Symptoms | Ascites[1] |
| Causes | Splenic vein thrombosis, stenosis of portal vein [2] |
| Diagnostic method | Ultrasonography[2] |
| Treatment | Portosystemic shunts, Nonselective beta-blockers[2] |
Portal hypertension is defined as increased portal venous pressure, with a hepatic venous pressure gradient greater than 5 mmHg.[3][4] Normal portal pressure is 1–4 mmHg; clinically insignificant portal hypertension is present at portal pressures 5–9 mmHg; clinically significant portal hypertension is present at portal pressures greater than 10 mmHg.[5] The portal vein and its branches supply most of the blood and nutrients from the intestine to the liver.[6]
Cirrhosis (a form of chronic liver failure) is the most common cause of portal hypertension; other, less frequent causes are therefore grouped as non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. The signs and symptoms of both cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic portal hypertension are often similar depending on cause, with patients presenting with abdominal swelling due to ascites, vomiting of blood, and lab abnormalities such as elevated liver enzymes or low platelet counts.
Treatment is directed towards decreasing portal hypertension itself or in the management of its acute and chronic complications.[7] Complications include ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, variceal hemorrhage, hepatic encephalopathy, hepatorenal syndrome, and cardiomyopathy.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
patientwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
emedwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ D'Souza D. "Portal hypertension". Radiopaedia. Retrieved 11 March 2021.
- ^ "Portal hypertension | Disease | Overview". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2016-01-27. Retrieved 2016-01-08.
- ^ Kibrit J, Khan R, Jung BH, Koppe S (August 2018). "Clinical Assessment and Management of Portal Hypertension". Seminars in Interventional Radiology. 35 (3): 153–159. doi:10.1055/s-0038-1660793. PMC 6078702. PMID 30087517.
- ^ "Portal Hypertension - Liver and Gallbladder Disorders". MSD Manual Consumer Version. Retrieved 11 March 2021.
- ^ Kulkarni AV, Rabiee A, Mohanty A (July 2022). "Management of Portal Hypertension". Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hepatology. 12 (4): 1184–1199. doi:10.1016/j.jceh.2022.03.002. PMC 9257868. PMID 35814519.