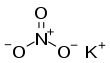Back Kaliumnitraat Afrikaans نترات البوتاسيوم Arabic যখাৰ Assamese Nitratu de potasiu AST Kalium nitrat Azerbaijani پوتاسیوم نیترات AZB Калиев нитрат Bulgarian পটাশিয়াম নাইট্রেট Bengali/Bangla Kalij-nitrat BS Nitrat de potassi Catalan

| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium nitrate
| |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.926 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| E number | E252 (preservatives) | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1486 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| KNO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 101.1032 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | white solid | ||
| Odor | odorless | ||
| Density | 2.109 g/cm3 (16 °C) | ||
| Melting point | 334 °C (633 °F; 607 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 400 °C (752 °F; 673 K) (decomposes) | ||
| 133 g/1000 g water (0 °C) 316 g/1000 g water (20 °C) 383 g/1000 g water (25 °C) 2439 g/1000 g water (100 °C)[2] | |||
| Solubility | slightly soluble in ethanol soluble in glycerol, ammonia | ||
| Basicity (pKb) | 15.3[3] | ||
| −33.7·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.335, 1.5056, 1.5604 | ||
| Structure | |||
| Orthorhombic, Aragonite | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Heat capacity (C)
|
95.06 J/mol K | ||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-494.00 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
Oxidant, harmful if swallowed, inhaled, or absorbed on skin. Causes irritation to skin and eye area. | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| H272, H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P102, P210, P220, P221, P280 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | non-flammable (oxidizer) | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
1901 mg/kg (oral, rabbit) 3750 mg/kg (oral, rat)[4] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | ICSC 0184 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Other anions
|
Potassium nitrite | ||
Other cations
|
Lithium nitrate Sodium nitrate Rubidium nitrate Caesium nitrate | ||
Related compounds
|
Potassium sulfate Potassium chloride | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Potassium nitrate (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with a sharp, salty, bitter taste and the chemical formula KNO
3. It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrate ions NO3−, and is therefore an alkali metal nitrate. It occurs in nature as a mineral, niter (or nitre outside the US).[5] It is a source of nitrogen, and nitrogen was named after niter. Potassium nitrate is one of several nitrogen-containing compounds collectively referred to as saltpetre (or saltpeter in the US).[5]
Major uses of potassium nitrate are in fertilizers, tree stump removal, rocket propellants and fireworks. It is one of the major constituents of gunpowder (black powder).[6] In processed meats, potassium nitrate reacts with hemoglobin and myoglobin generating a red color.[7]
- ^ Record of Potassium nitrate in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, accessed on 2007-03-09.
- ^ B. J. Kosanke; B. Sturman; K. Kosanke; et al. (2004). "2". Pyrotechnic Chemistry. Journal of Pyrotechnics. pp. 5–6. ISBN 978-1-889526-15-7. Archived from the original on 2016-05-05.
- ^ Kolthoff, Treatise on Analytical Chemistry, New York, Interscience Encyclopedia, Inc., 1959.
- ^ Ema, M.; Kanoh, S. (1983). "[Studies on the pharmacological bases of fetal toxicity of drugs. III. Fetal toxicity of potassium nitrate in 2 generations of rats]". Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. Folia Pharmacologica Japonica. 81 (6): 469–480. doi:10.1254/fpj.81.469. ISSN 0015-5691. PMID 6618340.
- ^ a b Shorter Oxford English Dictionary (6th ed.). United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. 2007. p. 3804. ISBN 9780199206872.
- ^ Lauer, Klaus (1991). "The history of nitrite in human nutrition: A contribution from German cookery books". Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. 44 (3): 261–264. doi:10.1016/0895-4356(91)90037-a. ISSN 0895-4356. PMID 1999685.
- ^ Haldane, J. (1901). "The Red Colour of Salted Meat". The Journal of Hygiene. 1 (1): 115–122. doi:10.1017/S0022172400000097. ISSN 0022-1724. PMC 2235964. PMID 20474105.