
Back البرنامج الدولي لتقييم الطلبة Arabic Informe PISA AST Програма за международно оценяване на учениците Bulgarian Programa PISA Catalan PISA Czech Rhaglen Ryngwladol Asesu Myfyrwyr Welsh PISA (elevvurdering) Danish PISA-Studien German PISA Esperanto Informe PISA Spanish
| Abbreviation | PISA |
|---|---|
| Formation | 1997 |
| Purpose | Comparison of education attainment across the world |
| Headquarters | OECD Headquarters |
| Location |
|
Region served | World |
Membership | 79 government education departments |
Official language | English and French |
Head of the Early Childhood and Schools Division | Yuri Belfali |
Main organ | PISA Governing Body (Chair – Michele Bruniges) |
Parent organization | OECD |
| Website | www |
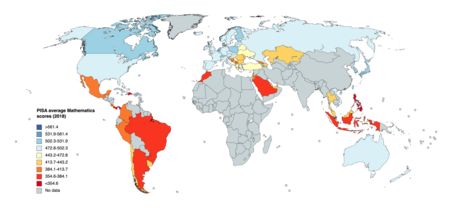
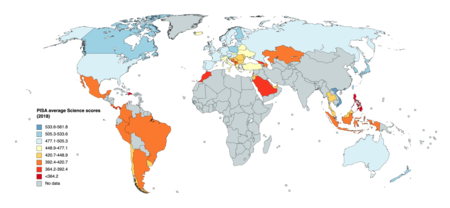

The Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA) is a worldwide study by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) in member and non-member nations intended to evaluate educational systems by measuring 15-year-old school pupils' scholastic performance on mathematics, science, and reading.[1] It was first performed in 2000 and then repeated every three years. Its aim is to provide comparable data with a view to enabling countries to improve their education policies and outcomes. It measures problem solving and cognition.[2]
The results of the 2022 data collection were released in December 2023.[3]
- ^ "About PISA". OECD PISA. Retrieved 8 February 2018.
- ^ Berger, Kathleen (3 March 2014). Invitation to The Life Span (second ed.). worth. ISBN 978-1-4641-7205-2.
- ^ "PISA 2022 Results". OECD. December 2023. Archived from the original on 5 December 2023. Retrieved 15 December 2023.