
Back 30S Catalan زیرواحد ۳۰اس ریبوزوم پروکاریوتی Persian Sous-unité ribosomique 30S French 30S Portuguese 30S Serbo-Croatian 30S Serbian 30S核糖体亚基 Chinese
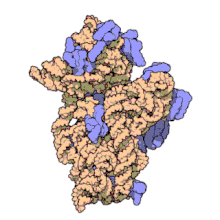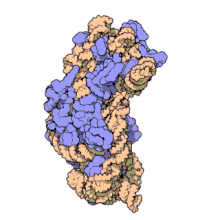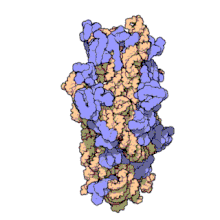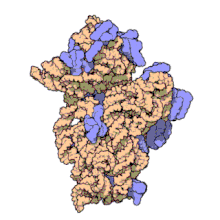
The prokaryotic small ribosomal subunit, or 30S subunit, is the smaller subunit of the 70S ribosome found in prokaryotes. It is a complex of the 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and 19 proteins.[1] This complex is implicated in the binding of transfer RNA to messenger RNA (mRNA).[2] The small subunit is responsible for the binding and the reading of the mRNA during translation. The small subunit, both the rRNA and its proteins, complexes with the large 50S subunit to form the 70S prokaryotic ribosome in prokaryotic cells. This 70S ribosome is then used to translate mRNA into proteins.
- ^ a b Schluenzen, Frank; Tocilj, Ante; Zarivach, Raz; Harms, Joerg; Gluehmann, Marco; Janell, Daniela; Bashan, Anat; Bartels, Heike; Agmon, Ilana (2000-09-01). "Structure of Functionally Activated Small Ribosomal Subunit at 3.3 Å Resolution". Cell. 102 (5): 615–623. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00084-2. PMID 11007480.
- ^ Thompson, John F.; Hearst (1983). "Structure-Function Relations in E. coli 16s RNA" (PDF). Cell. 33 (1): 19–24. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.625.7760. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(83)90330-6. PMID 6380748. S2CID 13069755.