
Back Pneumolochía AN طب الرئة Arabic منظمات النفس ARZ Neumoloxía AST Pulmonologiya Azerbaijani Пульманалогія Byelorussian Пульманалёгія BE-X-OLD Пулмология Bulgarian Pneumologia Catalan پزیشکیی سی CKB
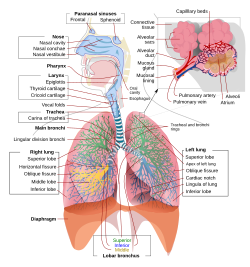 Schematic view of the human respiratory system with their parts and functions. | |
| System | Respiratory |
|---|---|
| Significant diseases | Asthma, Lung cancer, Tuberculosis, Occupational lung disease |
| Significant tests | Bronchoscopy, Sputum studies, Arterial blood gases |
| Specialist | Respiratory Physician, Pulmonologist |
Pulmonology (/ˌpʌlməˈnɒlədʒi/, /ˌpʊlməˈnɒlədʒi/, from Latin pulmō, -ōnis "lung" and the Greek suffix -λογία -logía "study of"), pneumology (/nʊˈmɒlədʒi, njʊ-/, built on Greek πνεύμων pneúmōn "lung") or pneumonology[1] (/nʊmənˈɒlədʒi, njʊ-/) is a medical specialty that deals with diseases involving the respiratory tract.[2] It is also known as respirology, respiratory medicine, or chest medicine in some countries and areas.
Pulmonology is considered a branch of internal medicine, and is related to intensive care medicine. Pulmonology often involves managing patients who need life support and mechanical ventilation. Pulmonologists are specially trained in diseases and conditions of the chest, particularly pneumonia, asthma, tuberculosis, emphysema, and complicated chest infections.[3]
Pulmonology/respirology departments work especially closely with certain other specialties: cardiothoracic surgery departments and cardiology departments.
- ^ Ramoutsaki, Ioanna; Ramoutsakis, Ioannis; Bouros, Demosthenes (May 2002). "Pneumonology or Pneumology?". Chest. 121 (5): 1385–1387. doi:10.1378/chest.121.5.1385. PMID 12006412.
- ^ ACP: Pulmonology: Internal Medicine Subspecialty Archived 2015-08-11 at the Wayback Machine. Acponline.org. Retrieved on 2011-09-30.
- ^ Sengupta, Nandini; Sahidullah, Md; Saha, Goutam (August 2016). "Lung sound classification using cepstral-based statistical features". Computers in Biology and Medicine. 75 (1): 118–129. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2016.05.013. PMID 27286184.