
Back بوليميراز الرنا II Arabic RNK-polimeraza II BS ARN polimerasa II Catalan RNA polymeráza II Czech RNA-Polymerase II German ARN polimerasa II Spanish RNA polümeraas II Estonian آرانای پلیمراز II Persian ARN polymérase II French ARN polimerase II Galician
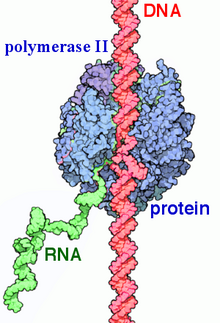
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA.[1][2] It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.[3] A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase. A wide range of transcription factors are required for it to bind to upstream gene promoters and begin transcription.
- ^ Kornberg RD (December 1999). "Eukaryotic transcriptional control". Trends in Cell Biology. 9 (12): M46–9. doi:10.1016/S0962-8924(99)01679-7. PMID 10611681.
- ^ Sims RJ, Mandal SS, Reinberg D (June 2004). "Recent highlights of RNA-polymerase-II-mediated transcription". Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 16 (3): 263–71. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2004.04.004. PMID 15145350.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
:0was invoked but never defined (see the help page).