
Back Richard II van Engeland Afrikaans Ricardo II d'Anglaterra AN Riċheard II Engla Cyning ANG ريتشارد الثاني (ملك إنجلترا) Arabic ريتشارد التانى ملك انجلترا ARZ II Riçard Azerbaijani ایکینجی ریچارد (اینگیلیس) AZB Рычард II Byelorussian Ричард II Bulgarian Richarzh II (Bro-Saoz) Breton
| Richard II | |
|---|---|
 Portrait at Westminster Abbey, mid-1390s[a] | |
| King of England | |
| Reign | 21 June 1377 – 29 September 1399 |
| Coronation | 16 July 1377 |
| Predecessor | Edward III |
| Successor | Henry IV |
| Born | 6 January 1367 Bordeaux, France |
| Died | c. 14 February 1400 (aged 33) Pontefract Castle, Yorkshire, England |
| Burial | |
| Spouses | |
| House | Plantagenet |
| Father | Edward the Black Prince |
| Mother | Joan of Kent |
| Signature | 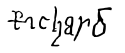 |
Richard II (6 January 1367 – c. 14 February 1400), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward, Prince of Wales (later known as the Black Prince), and Joan, Countess of Kent. Richard's father died in 1376, leaving Richard as heir apparent to his grandfather, King Edward III; upon the latter's death, the 10-year-old Richard succeeded to the throne.
During Richard's first years as king, government was in the hands of a series of regency councils, influenced by Richard's uncles John of Gaunt and Thomas of Woodstock. England at that time faced various problems, most notably the Hundred Years' War. A major challenge of the reign was the Peasants' Revolt in 1381, and the young king played a central part in the successful suppression of this crisis. Less warlike than either his father or grandfather, he sought to bring an end to the Hundred Years' War. A firm believer in the royal prerogative, Richard restrained the power of the aristocracy and relied on a private retinue for military protection instead. In contrast to his grandfather, Richard cultivated a refined atmosphere centred on art and culture at court, in which the king was an elevated figure.
The King's dependence on a small number of courtiers caused discontent among the nobility, and in 1387 control of government was taken over by a group of aristocrats known as the Lords Appellant. By 1389 Richard had regained control, and for the next eight years governed in relative harmony with his former opponents. In 1397, he took his revenge on the Appellants, many of whom were executed or exiled. The next two years have been described by historians as Richard's "tyranny". In 1399, after John of Gaunt died, the King disinherited Gaunt's son Henry Bolingbroke, who had previously been exiled. Henry invaded England in June 1399 with a small force that quickly grew in numbers. Meeting little resistance, he deposed Richard and had himself crowned king. Richard is thought to have been starved to death in captivity, although questions remain regarding his final fate.
Richard's posthumous reputation has been shaped to a large extent by William Shakespeare, whose play Richard II portrayed Richard's misrule and his deposition as responsible for the 15th-century Wars of the Roses. Modern historians do not accept this interpretation, while not exonerating Richard from responsibility for his own deposition. While probably not insane, as many historians of the 19th and 20th centuries believed him to be, he may have had a personality disorder, particularly manifesting itself towards the end of his reign. Most authorities agree that his policies were not unrealistic or even entirely unprecedented, but that the way in which he carried them out was unacceptable to the political establishment, leading to his downfall.
- ^ "Richard II and Anne of Bohemia". Westminster Abbey. Retrieved 17 October 2022.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).