
Back Modulació en anell Catalan Ringmodulator German Modulation en anneau French Ringmodulatie Dutch Кольцевая модуляция Russian Ringmodulator Swedish Кільцева модуляція Ukrainian
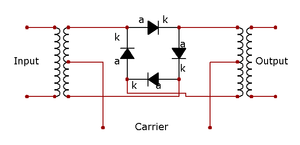

In electronics, ring modulation is a signal processing function, an implementation of frequency mixing, in which two signals are combined to yield an output signal. One signal, called the carrier, is typically a sine wave or another simple waveform; the other signal is typically more complicated and is called the input or the modulator signal. A ring modulator is an electronic device for ring modulation. A ring modulator may be used in music synthesizers and as an effects unit.
The name derives from the fact that the analog circuit of diodes originally used to implement this technique takes the shape of a ring: a diode ring.[2] The circuit is similar to a bridge rectifier, except that instead of the diodes facing left or right, they face clockwise or counterclockwise.
Ring modulation is quite similar to amplitude modulation, with the difference that in the latter the modulator is shifted to be positive before being multiplied with the carrier, while in the former the unshifted modulator is multiplied with the carrier. This has the effect that ring modulation of two sine waves having frequencies of 1,500 Hz and 400 Hz will produce as output signal the sum of a sine wave with frequency 1,900 Hz and one with frequency 1,100 Hz. These two output frequencies are known as sidebands. If one of the input signals has significant overtones (which is the case for square waves), the output will sound quite different, since each harmonic will generate its own pair of sidebands that won't be harmonically-related.[3]
- ^ Curtis Roads (1996). The Computer Music Tutorial, pp. 220-221. MIT Press. ISBN 9780262680820.
- ^ Richard Orton, "Ring Modulator", The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians, page 429, volume 21, second edition, edited by Stanley Sadie and John Tyrrell (London: Macmillan Publishers, 2001): "the ring modulator takes its name from the characteristic ring formation of four diodes in its analog circuit."
- ^ Strange, Allen (1972). Electronic Music, p. 11. Wm. C. Brown Co. Publishers. ISBN 0-697-03612-X.

