
Back Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 Czech رولز-رویس/سنکما الیمپوس ۵۹۳ Persian Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 French Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 ID Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 Italian ロールス・ロイス/スネクマ オリンパス 593 Japanese Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 Polish Rolls-Royce/SNECMA Olympus 593 Russian Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 Slovenian Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 Ukrainian
| Olympus 593 | |
|---|---|
| |
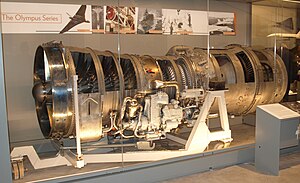
| On display at the Aerospace Bristol museum | |
| Type | Turbojet |
| National origin | United Kingdom/France |
| Manufacturer | Rolls-Royce Limited/Snecma |
| First run | June 1966 |
| Major applications | Concorde |
| Developed from | Rolls-Royce Olympus |
The Rolls-Royce/Snecma Olympus 593 was an Anglo-French turbojet with reheat, which powered the supersonic airliner Concorde. It was initially a joint project between Bristol Siddeley Engines Limited (BSEL) and Snecma, derived from the Bristol Siddeley Olympus 22R engine.[1][2] Rolls-Royce Limited acquired BSEL in 1966 during development of the engine, making BSEL the Bristol Engine Division of Rolls-Royce.[2]
Until regular commercial flights by Concorde ceased in October 2003, the Olympus turbojet was unique in aviation as the only turbojet with reheat powering a commercial aircraft.
The overall efficiency of the engine in supersonic cruising flight (supercruise) was about 43%, which at the time was the highest figure recorded for any normal thermodynamic machine.[3]
- ^ "Olympus-the first forty years" Alan Baxter, RRHT No15, ISBN 978-0-9511710-9-7, p. 135.
- ^ a b Leney, David; Macdonald, David (July 2020). Aérospatiale/BAC Concorde 1969 onwards (all models). Sparkford, Somerset: Haynes Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84425-818-5.
- ^ Hooker, Stanley (1984). Not much of an Engineer: an autobiography. Assisted by Bill Gunston. Shrewsbury, England: Airlife. pp. 154–155. ISBN 9780906393352. OCLC 11437258.