
Back SN 1572 Afrikaans مستعر أعظم 1572 Arabic SN 1572 Catalan SN 1572 Czech SN 1572 Danish SN 1572 German SN 1572 Spanish SN 1572 Estonian اسان ۱۵۷۲ Persian SN 1572 Finnish
 | |
| Event type | Astronomical radio source, astrophysical X-ray source |
|---|---|
| Type Ia[1] | |
| Date | November 1572 |
| Constellation | Cassiopeia |
| Right ascension | 0h 25.3m |
| Declination | +64° 09′ |
| Epoch | ? |
| Galactic coordinates | G.120.1+1.4 |
| Distance | between 8,000 ly (2.5 kpc) and 9,800 ly (3 kpc) |
| Remnant | Nebula |
| Host | Milky Way |
| Progenitor | Unknown |
| Progenitor type | Unknown |
| Colour (B-V) | ~1 |
| Peak apparent magnitude | −4 |
| Other designations | SN 1572, HR 92, SN 1572A, SNR G120.1+01.4, SNR G120.2+01.4, 1ES 0022+63.8, 1RXS J002509.2+640946, B Cas, BD+63 39a, 8C 0022+638, 4C 63.01, 3C 10, 3C 10.0, 2C 34, RRF 1174, 1XRS 00224+638, 2U 0022+63, 3A 0022+638, 3CR 10, 3U 0022+63, 4U 0022+63, AJG 112, ASB 1, BG 0022+63, CTB 4, KR 101, VRO 63.00.01, [DGW65] 3, PBC J0024.9+6407, F3R 3628, WB 0022+6351, CGPSE 107, GB6 B0022+6352 |
| Preceded by | SN 1181 |
| Followed by | SN 1604 |
| | |
Preview warning: Page using Template:Infobox astronomical event with unknown parameter "image_size"
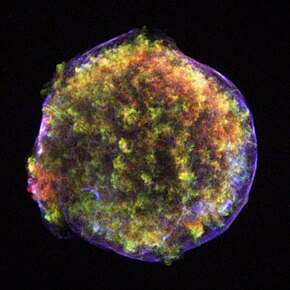
SN 1572 (Tycho's Supernova, Tycho's Nova), or B Cassiopeiae (B Cas), was a supernova of Type Ia in the constellation Cassiopeia, one of eight supernovae visible to the naked eye in historical records. It appeared in early November 1572 and was independently discovered by many individuals.
Its supernova remnant has been observed optically but was first detected at radio wavelengths. It is often known as 3C 10, a radio-source designation, although increasingly as Tycho's supernova remnant.