
Back ثقافات سكيثية Arabic فرهنگهای سکایی Persian 스키타이 문화 Korean Scythisch-Siberische wereld Dutch Скифо-сибирский мир Russian Скіфо-сибірський світ Ukrainian
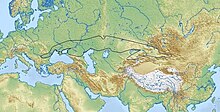 | |
| Geographical range | Eurasian Steppe |
|---|---|
| Period | Iron Age |
| Dates | c. 900 BC–200 AD |
| Preceded by | Srubnaya culture, Andronovo culture |
| Followed by | Goths, Alans, Xiongnu, Circassians |
The Scytho-Siberian world[1][a] was an archaeological horizon that flourished across the entire Eurasian Steppe during the Iron Age, from approximately the 9th century BC to the 2nd century AD. It included the Scythian, Sauromatian and Sarmatian cultures of Eastern Europe, the Saka-Massagetae and Tasmola cultures of Central Asia, and the Aldy-Bel, Pazyryk and Tagar cultures of south Siberia.
The Scythian-Siberian world was characterized by the Scythian triad, which are similar, yet not identical, styles of weapons, horses' bridles, and jewelry and decorative art. The question of how related these cultures were is disputed among scholars. Its peoples were of diverse origins, and included not just Scythians, from which the cultures are named, but other peoples as well, such as the Cimmerians, Massagetae, Saka, Sarmatians, and obscure forest-steppe populations. Mostly speakers of the Scythian branch of the Iranian languages,[b] all of these peoples are sometimes collectively referred to as Scythians, Scytho-Siberians, Early Nomads, or Iron Age Nomads.[3]
- ^ Alekseyev, Andrey [in Russian] (2017). "Scytho-Siberian world". Great Russian Encyclopedia (in Russian).
- ^ Simpson 2017.
- ^ Unterländer 2017. Genomic inference reveals that Scythians in the east and the west of the steppe zone can best be described as a mixture of Yamnaya-related ancestry and an East Asian component. Demographic modelling suggests independent origins for eastern and western groups with ongoing gene-flow between them, plausibly explaining the striking uniformity of their material culture. We also find evidence that significant gene-flow from east to west Eurasia must have occurred early during the Iron Age. The origin of the widespread Scythian-Siberian cultures has long been debated in Eurasian archaeology. The northern Black Sea steppe was originally considered the homeland and centre of the Scythians3 until Terenozhkin formulated the hypothesis of a Central Asian origin4. On the other hand, evidence supporting an east Eurasian origin includes the kurgan Arzhan 1 in Tuva5, which is considered the earliest Scythian kurgan5. Dating of additional burial sites situated in east and west Eurasia confirmed eastern kurgans as older than their western counterparts6,7. Additionally, elements of the characteristic 'Animal Style' dated to the tenth century BCE1,4 were found in the region of the Yenisei river and modern-day China, supporting the early presence and origin of Scythian culture in the East.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).