
Back شو (حرف) Arabic Ϸ ARC Scho BAR Шо (літара) Byelorussian Шо (літара) BE-X-OLD Шо (буква) Bulgarian Sho (lizherenn) Breton Ϸ Catalan شۆ (پیت) CKB Šo Czech
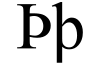 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Greek alphabet | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diacritics and other symbols | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Related topics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The letter ϸ (sometimes called sho or san) was a letter added to the Greek alphabet in order to write the Bactrian language.[1] It was similar in appearance to the Anglo-Saxon and Icelandic letter thorn (þ), which has typically been used to represent it in modern print, although both are historically quite unrelated. It probably represented a sound similar to English "sh" ([ʃ]). Its conventional transliteration in Latin is ⟨š⟩.[2]


Its original name and position in the Bactrian alphabet, if it had any, are unknown. Some authors have called it "san", on the basis of the hypothesis that it was a survival or reintroduction of the archaic Greek letter San.[3] This letter ϸ closely resembles, perhaps coincidentally, the letter ⟨𐊮⟩ of the Greek-based Carian alphabet which may have also stood for [ʃ]. The name "sho" was coined for the letter for purposes of modern computer encoding in 2002, on the basis of analogy with "rho" (ρ), the letter with which it seems to be graphically related.[1] Ϸ was added to Unicode in version 4.0 (2003), in an uppercase and lowercase character designed for modern typography.
- ^ a b c Everson, M. and Sims-Williams, N. (2002) “Proposal to add two Greek letters for Bactrian to the UCS”,ISO/IEC JTC1/SC2/WG2 N2411.
- ^ Skjærvø, P. O. (2009). "Bactrian". In Brown, Keith; Ogilvie, Sarah (eds.). Concise encyclopedia of languages of the world. Oxford: Elsevier. p. 115. ISBN 9780080877754.
- ^ Tarn, William Woodthorpe (1961). The Greeks in Bactria and India. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 508. ISBN 9781108009416.