
Back وراکروز موحاصیرهسی AZB Belejringen af Veracruz Danish Asedio de Veracruz Spanish محاصره وراکروز Persian Siège de Veracruz (1847) French Sitio de Veracruz Galician Pengepungan Veracruz ID Assedio di Veracruz Italian ベラクルス包囲戦 Japanese Cerco de Veracruz Portuguese
| Siege of Veracruz | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Mexican–American War | |||||||
 Scott's siege guns were in place on ground outside the city | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| United States | Mexico | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Winfield Scott David Conner Matthew C. Perry | Juan Esteban Morales | ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| See order of battle | See order of battle | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 8,600[1] | 3,360[1] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
13 killed 55 wounded[1][2] |
80[1]–350 killed 50 wounded[2] 3,000 captured | ||||||
| 100–1,000 civilians killed[1] | |||||||
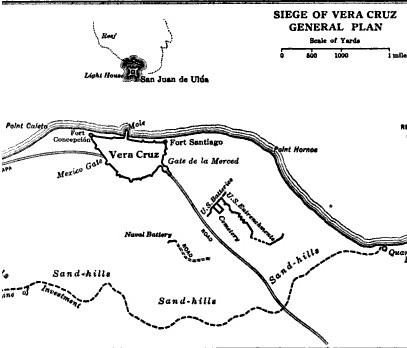
On 9 March 1847, during the Mexican–American War, the United States military made an amphibious landing and besieged the key Mexican seaport of Veracruz. The port surrendered twenty days later. The U.S. forces then marched inland to Mexico City.