
Back ጨው Amharic كلوريد الصوديوم Arabic Cloruru de sodiu AST Натриялъул хлорид AV Natrium xlorid Azerbaijani کولورید سودیوم AZB Sodium chloride BCL Натриев хлорид Bulgarian সোডিয়াম ক্লোরাইড Bengali/Bangla Natrij-hlorid BS
 Sodium chloride crystals in a form of halite
| |
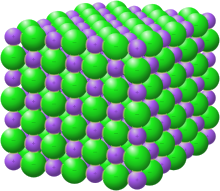 Crystal structure with sodium in purple and chloride in green[1]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium chloride
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3534976 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.726 |
| EC Number |
|
| 13673 | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Sodium+chloride |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NaCl | |
| Molar mass | 58.443 g/mol[2] |
| Appearance | Colorless cubic crystals[2] |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 2.17 g/cm3[2] |
| Melting point | 800.7 °C (1,473.3 °F; 1,073.8 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 1,465 °C (2,669 °F; 1,738 K)[2] |
| 360 g/L (25°C)[2] | |
| Solubility in ammonia | 21.5 g/L |
| Solubility in methanol | 14.9 g/L |
| −30.2·10−6 cm3/mol[3] | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5441 (at 589 nm)[4] |
| Structure[5] | |
| Face-centered cubic (see text), cF8 | |
| Fm3m (No. 225) | |
a = 564.02 pm
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
4 |
| octahedral at Na+ octahedral at Cl− | |
| Thermochemistry[6] | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
50.5 J/(K·mol) |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
72.10 J/(K·mol) |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−411.120 kJ/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| A12CA01 (WHO) B05CB01 (WHO), B05XA03 (WHO), S01XA03 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
3 g/kg (oral, rats)[7] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Sodium fluoride Sodium bromide Sodium iodide Sodium astatide |
Other cations
|
Lithium chloride Potassium chloride Rubidium chloride Caesium chloride Francium chloride |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Sodium chloride (data page) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sodium chloride /ˌsoʊdiəm ˈklɔːraɪd/,[8] commonly known as edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chlorine ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs as the mineral halite. In its edible form, it is commonly used as a condiment and food preservative. Large quantities of sodium chloride are used in many industrial processes, and it is a major source of sodium and chlorine compounds used as feedstocks for further chemical syntheses. Another major application of sodium chloride is deicing of roadways in sub-freezing weather.
- ^ "Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Crystal". PhysicsOpenLab. Retrieved 23 August 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f Haynes, 4.89
- ^ Haynes, 4.135
- ^ Haynes, 10.241
- ^ Haynes, 4.148
- ^ Haynes, 5.8
- ^ Tucker, R. K.; Haegele, M. A. (1971). "Comparative acute oral toxicity of pesticides to six species of birds". Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 20 (1): 57–65. Bibcode:1971ToxAP..20...57T. doi:10.1016/0041-008x(71)90088-3. ISSN 0041-008X. PMID 5110827.
- ^ Wells, John C. (2008), Longman Pronunciation Dictionary (3rd ed.), Longman, pp. 143 and 755, ISBN 9781405881180
