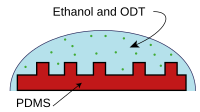


In technology, soft lithography is a family of techniques for fabricating or replicating structures using "elastomeric stamps, molds, and conformable photomasks".[1] It is called "soft" because it uses elastomeric materials, most notably PDMS.
Soft lithography is generally used to construct features measured on the micrometer to nanometer scale. According to Rogers and Nuzzo (2005), development of soft lithography expanded rapidly from 1995 to 2005. Soft lithography tools are now commercially available.[2]
- ^ In the words of Rogers and Nuzzo, p. 50, as cited in "Further reading"
- ^ "Research Micro Stamps: Commercially available micro stamps on tv". RMS. Retrieved 2017-01-17.
