
Back نواة مفردة Arabic Nucleus tractus solitarii German Núcleo del tracto solitario Spanish Noyau du faisceau solitaire French Solitarna jezgra Croatian Nucleus tractus solitarii Hungarian Nucleo del tratto solitario Italian 고립로핵 Korean Jądro pasma samotnego Polish Núcleo do trato solitário Portuguese
| Solitary nucleus | |
|---|---|
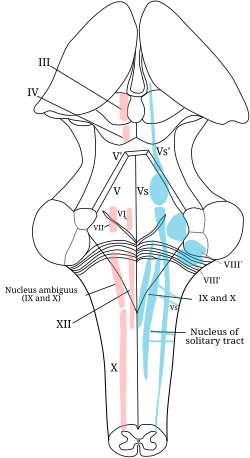 The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue. | |
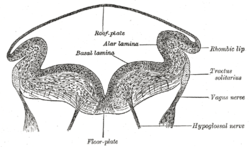 Transverse section of medulla oblongata of human embryo. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nucleus tractus solitarii medullae oblongatae |
| MeSH | D017552 |
| NeuroNames | 742 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1429 |
| TA98 | A14.1.04.230 |
| TA2 | 6008 |
| FMA | 72242 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The solitary nucleus (also called nucleus of the solitary tract, nucleus solitarius, or nucleus tractus solitarii (SN or NTS))[1][2] is a series of sensory nuclei (clusters of nerve cell bodies) forming a vertical column of grey matter in the medulla oblongata of the brainstem. It receives general visceral and/or special visceral inputs from the facial nerve (CN VII), glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) and vagus nerve (CN X); it receives and relays stimuli related to taste and visceral sensation. It sends outputs to various parts of the brain, such as the hypothalamus, thalamus, and reticular formation. Neuron cell bodies of the SN are roughly somatotopically arranged along its length according to function.
- ^ Duane E. Haines (2004). Neuroanatomy: An Atlas of Structures, Sections, and Systems. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 186–. ISBN 978-0-7817-4677-9. Retrieved 22 January 2013.
- ^ P. Michael Conn (2008). Neuroscience in Medicine. Springer. p. 264. ISBN 978-1-60327-455-5. Retrieved 22 January 2013.