Back Spica Afrikaans السماك الأعزل Arabic Spica AST Spika Azerbaijani Спіка Byelorussian Спика Bulgarian Spika (zvijezda) BS Spica Catalan Spica Czech Spica Danish
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Virgo |
| Pronunciation | /ˈspaɪkə/ or /ˈspiːkə/[1][2] |
| Right ascension | 13h 25m 11.579s[3] |
| Declination | −11° 09′ 40.75″[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | +0.97[4] (0.97–1.04[5]) |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B1III-IV + B2V[6] |
| U−B color index | −0.94[4] |
| B−V color index | −0.23[4] |
| Variable type | β Cep + Ellipsoidal[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +1.0[7] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −42.35±0.62[3] mas/yr Dec.: −30.67±0.37[3] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 13.06 ± 0.70 mas[3] |
| Distance | 250 ± 10 ly (77 ± 4 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −3.55 (−3.5/−1.5)[8] |
| Orbit[9] | |
| Period (P) | 4.0145±0.0001 d |
| Semi-major axis (a) | 28.20±0.92 R☉ |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.133±0.017 |
| Inclination (i) | 63.1±2.5° |
| Periastron epoch (T) | 2,454,189.4±0.02 |
| Argument of periastron (ω) (secondary) | 255.6±12.2° |
| Details[9] | |
| Primary | |
| Mass | 11.43±1.15 M☉ |
| Radius | 7.47±0.54 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 20,512+5,015 −4,030 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.71±0.10 cgs |
| Temperature | 25,300±500 K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 165.3±4.5 km/s |
| Age | 12.5 Myr |
| Secondary | |
| Mass | 7.21±0.75 M☉ |
| Radius | 3.74±0.53 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 2,254+1,166 −768 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 4.15±0.15 cgs |
| Temperature | 20,900±800 K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 58.8±1.5 km/s |
| Other designations | |
Spica, Azimech, Spica Virginis, α Virginis, Alpha Vir, 67 Virginis, BD−10°3672, FK5 498, HD 116658, HIP 65474, HR 5056, SAO 157923, CCDM 13252-1109[10] | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
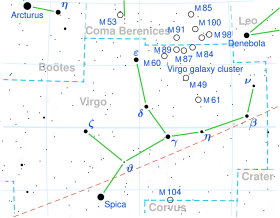
Spica is the brightest object in the constellation of Virgo and one of the 20 brightest stars in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation α Virginis, which is Latinised to Alpha Virginis and abbreviated Alpha Vir or α Vir. Analysis of its parallax shows that it is located 250±10 light-years from the Sun.[3] It is a spectroscopic binary star and rotating ellipsoidal variable; a system whose two stars are so close together they are egg-shaped rather than spherical, and can only be separated by their spectra. The primary is a blue giant and a variable star of the Beta Cephei type.
Spica, along with Arcturus and Denebola—or Regulus, depending on the source—forms the Spring Triangle asterism, and, by extension, is also part of the Great Diamond together with the star Cor Caroli.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
pronunciationwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
oxfordwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c d e f Cite error: The named reference
van Leeuwen2007was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
ducatiwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
rubanwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
bscwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
gcsrv53was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
mnras151was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Tkachenko2016was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
simbadwas invoked but never defined (see the help page).