
Back الجذر التربيعي ل 2 Arabic ২-এর বর্গমূল Bengali/Bangla Kvadratni korijen iz 2 BS Arrel quadrada de 2 Catalan ڕەگی دووەمی ٢ CKB Иккĕн тăваткалла тымарĕ CV Ail isradd 2 Welsh Quadratwurzel aus 2 German Τετραγωνική ρίζα του 2 Greek Kvadrata radiko de 2 Esperanto
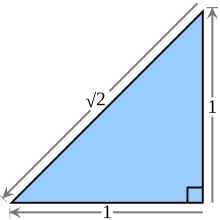 The square root of 2 is equal to the length of the hypotenuse of an isosceles right triangle with legs of length 1. | |
| Representations | |
|---|---|
| Decimal | 1.4142135623730950488... |
| Continued fraction | |
The square root of 2 (approximately 1.4142) is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself or squared, equals the number 2. It may be written in mathematics as or . It is an algebraic number, and therefore not a transcendental number. Technically, it should be called the principal square root of 2, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property.
Geometrically, the square root of 2 is the length of a diagonal across a square with sides of one unit of length; this follows from the Pythagorean theorem. It was probably the first number known to be irrational.[1] The fraction 99/70 (≈ 1.4142857) is sometimes used as a good rational approximation with a reasonably small denominator.
Sequence A002193 in the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences consists of the digits in the decimal expansion of the square root of 2, here truncated to 65 decimal places:[2]
- 1.41421356237309504880168872420969807856967187537694807317667973799
- ^ Fowler, David H. (1994). "The Story of the Discovery of Incommensurability, Revisited". In Gavroglu, Kostas; Christianidis, Jean; Nicolaidis, Efthymios (eds.). Trends in the Historiography of Science. Boston Studies in the Philosophy of Science. Vol. 151. Dortrecht: Springer. pp. 221–236. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-3596-4. ISBN 978-9048142644.
- ^ Sloane, N. J. A. (ed.). "Sequence A002193 (Decimal expansion of square root of 2)". The On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences. OEIS Foundation. Retrieved 2020-08-10.


