
Back مؤشر بورصة Arabic Índiz bursátil AST Борсов индекс Bulgarian Berzovni indeks BS Índex borsari Catalan Burzovní index Czech Aktieindeks Danish Aktienindex German Índice bursátil Spanish Börsiindeks Estonian
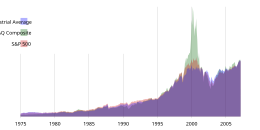
In finance, a stock index, or stock market index, is an index that measures the performance of a stock market, or of a subset of a stock market. It helps investors compare current stock price levels with past prices to calculate market performance.[1]
Two of the primary criteria of an index are that it is investable and transparent:[2] The methods of its construction are specified. Investors may be able to invest in a stock market index by buying an index fund, which is structured as either a mutual fund or an exchange-traded fund, and "track" an index. The difference between an index fund's performance and the index, if any, is called tracking error.
- ^ Caplinger, Dan (January 18, 2020). "What Is a Stock Market Index?". The Motley Fool.
- ^ Lo, Andrew W. (2016). "What Is an Index?". Journal of Portfolio Management. 42 (2): 21–36. doi:10.3905/jpm.2016.42.2.021. hdl:1721.1/109050. S2CID 219222815.