Back تفاعل استبدال Arabic Reaición de sustitución AST Reaksion əvəzlənmə Azerbaijani Алмаштырыу реакциялары Bashkir প্রতিস্থাপন বিক্রিয়া Bengali/Bangla Reacció de substitució Catalan کاردانەوەی گۆڕینەوە CKB Substituční reakce Czech Substitution (kemi) Danish Substitutionsreaktion German
A substitution reaction (also known as single displacement reaction or single substitution reaction) is a chemical reaction during which one functional group in a chemical compound is replaced by another functional group.[1] Substitution reactions are of prime importance in organic chemistry. Substitution reactions in organic chemistry are classified either as electrophilic or nucleophilic depending upon the reagent involved, whether a reactive intermediate involved in the reaction is a carbocation, a carbanion or a free radical, and whether the substrate is aliphatic or aromatic. Detailed understanding of a reaction type helps to predict the product outcome in a reaction. It also is helpful for optimizing a reaction with regard to variables such as temperature and choice of solvent.
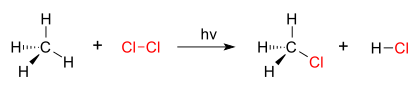
A good example of a substitution reaction is halogenation. When chlorine gas (Cl2) is irradiated, some of the molecules are split into two chlorine radicals (Cl•), whose free electrons are strongly nucleophilic. One of them breaks a C–H covalent bond in CH4 and grabs the hydrogen atom to form the electrically neutral HCl. The other radical reforms a covalent bond with the CH3• to form CH3Cl (methyl chloride).
| chlorination of methane by chlorine |
|---|
- ^ March, Jerry (1985), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure, 3rd edition, New York: Wiley, ISBN 9780471854722, OCLC 642506595