Back Tamil Afrikaans ታሚልኛ Amharic Idioma tamil AN तमिल भाषा ANP اللغة التاميلية Arabic التاميليه ARZ তামিল ভাষা Assamese Idioma tamil AST तमिल AWA Tamil dili Azerbaijani
Tamil[b] (தமிழ், Tamiḻ, pronounced [t̪amiɻ] ) is a classical Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. It is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India, along with Sanskrit,[10][11] attested since c. 300 BCE.[12][13][14][15][16]
The term "Tamil" has its origins in the ancient Tamil Sangams, where it was first recorded in the Tholkappiyam around the 2nd century BCE. The language belongs to the southern branch of the Dravidian language family and shares close ties with Malayalam and Kannada. Despite external influences, Tamil has retained a sense of linguistic purism, especially in formal and literary contexts.
Tamil was the lingua franca for early maritime traders, with inscriptions found in places like Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Egypt. The language has a well-documented history with literary works like Sangam literature, consisting of over 2,000 poems. Tamil script evolved from Tamil Brahmi, and later, the vatteluttu script was used until the current script was standardized. The language has a distinct grammatical structure, with agglutinative morphology that allows for complex word formations.
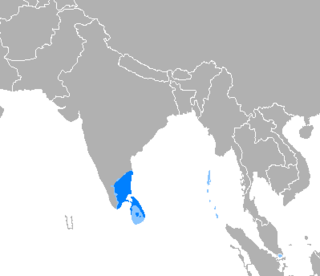
Tamil is predominantly spoken in Tamil Nadu, India, and the Northern and Eastern provinces of Sri Lanka. It has significant speaking populations in Malaysia, Singapore, and among diaspora communities. Tamil has been recognized as a classical language by the Indian government and holds official status in Tamil Nadu, Puducherry and Singapore. The language has seen efforts to purify it by reducing the influence of Sanskrit and other foreign loanwords. Tamil maintains its classical literary tradition while adapting to modern changes in colloquial speech and writing. Its phonology is characterized by a rich set of consonants and vowels, and it has a script that differs from other Indic scripts by its use of visible marks to indicate vowel omission.
- ^ Talbot 2001, pp. 27–37
- ^ a b Modern Tamil at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)

Old Tamil at Ethnologue (27th ed., 2024)
- ^ Official languages of Tamil Nadu, Tamil Nadu Government, archived from the original on 21 October 2012, retrieved 1 May 2007
- ^ Report of the Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities in India: 50th report (delivered to the Lokh Sabha in 2014) (PDF), National Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India., p. 155, archived from the original (PDF) on 8 July 2016, retrieved 8 June 2017
- ^ "Official Languages Policy". languagesdept.gov.lk. Department of Official Languages. Retrieved 20 May 2021.
- ^ Republic of Singapore Independence Act 1965 (No. 9 of 1965, 1985 Rev. Ed.), s7.
- ^ "Constitution of the Republic of South Africa, 1996 – Chapter 1: Founding Provisions", www.gov.za, South African Government
- ^ School languages, LINGUAMON, archived from the original on 2 September 2015, retrieved 26 March 2016
- ^ "Tamil, n. and adj". OED Online. Oxford University Press. Retrieved 24 January 2023.
- ^ Stein, B. (1977), "Circulation and the Historical Geography of Tamil Country", The Journal of Asian Studies, 37 (1): 7–26, doi:10.2307/2053325, JSTOR 2053325, S2CID 144599197. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7).
- ^ Steever 1998, p. 6. "one of India's two classical languages, alongside the more widely known Indo-Aryan language Sanskrit".
- ^ Definitive Editions of Ancient Tamil Works
- ^ Abraham, S.A. (2003), "Chera, Chola, Pandya: Using Archaeological Evidence to Identify the Tamil Kingdoms of Early Historic South India" (PDF), Asian Perspectives, 42 (2): 207, doi:10.1353/asi.2003.0031, hdl:10125/17189, S2CID 153420843
- ^ Zvelebil 1992, p. 12: "...the most acceptable periodisation which has so far been suggested for the development of Tamil writing seems to me to be that of A Chidambaranatha Chettiar (1907–1967): 1. Sangam Literature – 200BC to AD 200; 2. Post Sangam literature – AD 200 – AD 600; 3. Early Medieval literature – AD 600 to AD 1200; 4. Later Medieval literature – AD 1200 to AD 1800; 5. Pre-Modern literature – AD 1800 to 1900"
- ^ Maloney, C. (1970), "The Beginnings of Civilization in South India", The Journal of Asian Studies, 29 (3): 603–616, doi:10.2307/2943246, JSTOR 2943246, S2CID 162291987 at p. 610
- ^ Subramaniam, T.S. (29 August 2011), "Palani excavation triggers fresh debate", The Hindu, Chennai, India
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).