
Back Torus Afrikaans طارة (رياضيات) Arabic Tor (həndəsi fiqur) Azerbaijani Тор (геаметрыя) Byelorussian Тор (геометрия) Bulgarian Torus BS Tor (geometria) Catalan Toru (giumitria) Corsican Torus Czech Тор (çий) CV

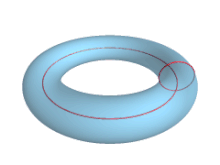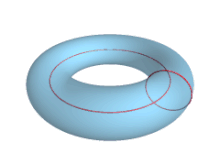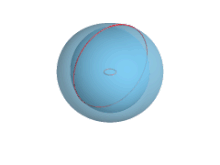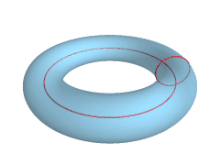

In geometry, a torus (pl.: tori or toruses) is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three-dimensional space one full revolution about an axis that is coplanar with the circle. The main types of toruses include ring toruses, horn toruses, and spindle toruses. A ring torus is sometimes colloquially referred to as a donut or doughnut.
If the axis of revolution does not touch the circle, the surface has a ring shape and is called a torus of revolution, also known as a ring torus. If the axis of revolution is tangent to the circle, the surface is a horn torus. If the axis of revolution passes twice through the circle, the surface is a spindle torus (or self-crossing torus or self-intersecting torus). If the axis of revolution passes through the center of the circle, the surface is a degenerate torus, a double-covered sphere. If the revolved curve is not a circle, the surface is called a toroid, as in a square toroid.
Real-world objects that approximate a torus of revolution include swim rings, inner tubes and ringette rings.
A torus should not be confused with a solid torus, which is formed by rotating a disk, rather than a circle, around an axis. A solid torus is a torus plus the volume inside the torus. Real-world objects that approximate a solid torus include O-rings, non-inflatable lifebuoys, ring doughnuts, and bagels.
In topology, a ring torus is homeomorphic to the Cartesian product of two circles: , and the latter is taken to be the definition in that context. It is a compact 2-manifold of genus 1. The ring torus is one way to embed this space into Euclidean space, but another way to do this is the Cartesian product of the embedding of in the plane with itself. This produces a geometric object called the Clifford torus, a surface in 4-space.
In the field of topology, a torus is any topological space that is homeomorphic to a torus.[1] The surface of a coffee cup and a doughnut are both topological tori with genus one.
An example of a torus can be constructed by taking a rectangular strip of flexible material such as rubber, and joining the top edge to the bottom edge, and the left edge to the right edge, without any half-twists (compare Klein bottle).
- ^ Gallier, Jean; Xu, Dianna (2013). A Guide to the Classification Theorem for Compact Surfaces. Geometry and Computing. Vol. 9. Springer, Heidelberg. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-34364-3. ISBN 978-3-642-34363-6. MR 3026641.

