
Back إصابة دماغية رضية Arabic Kəllə-beyin zədələnməsi Azerbaijani Чэрапна-мазгавая траўма Byelorussian Чэрапна-мазгавая траўма BE-X-OLD মস্তিষ্কের আঘাতজনিত জখম Bengali/Bangla Traumatisme cranioencefàlic Catalan Traumatické poranění mozku Czech Traumatisk hjerneskade Danish Schädel-Hirn-Trauma German Κρανιοεγκεφαλική κάκωση Greek
| Traumatic brain injury | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Intracranial injury, physically induced brain injury[1] |
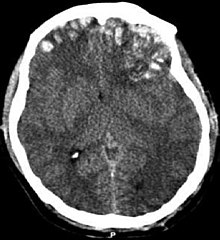 | |
| CT scan showing cerebral contusions, hemorrhage within the hemispheres, and subdural hematoma. There is also displaced skull fracture of left transverse parietal and temporal bones.[2] | |
| Specialty | Neurosurgery, pediatrics |
| Symptoms | Physical, cognitive, sensory, social, emotional, and behavioral symptoms |
| Types | Mild to severe[3] |
| Causes | Trauma to the head[3] |
| Risk factors | Old age,[3] alcohol |
| Diagnostic method | Based on neurological exam, medical imaging[4] |
| Treatment | Behavioral therapy, speech therapy |
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity ranging from mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI/concussion) to severe traumatic brain injury.[5] TBI can also be characterized based on mechanism (closed or penetrating head injury) or other features (e.g., occurring in a specific location or over a widespread area).[6] Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional and behavioral symptoms, and outcomes can range from complete recovery to permanent disability or death.
Causes include falls, vehicle collisions and violence. Brain trauma occurs as a consequence of a sudden acceleration or deceleration within the cranium or by a complex combination of both movement and sudden impact. In addition to the damage caused at the moment of injury, a variety of events following the injury may result in further injury. These processes may include alterations in cerebral blood flow and pressure within the skull. Some of the imaging techniques used for diagnosis of moderate to severe TBI include computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRIs).
Prevention measures include use of seat belts and helmets, not drinking and driving, fall prevention efforts in older adults and safety measures for children.[7] Depending on the injury, treatment required may be minimal or may include interventions such as medications, emergency surgery or surgery years later. Physical therapy, speech therapy, recreation therapy, occupational therapy and vision therapy may be employed for rehabilitation. Counseling, supported employment and community support services may also be useful.
TBI is a major cause of death and disability worldwide, especially in children and young adults.[8] Males sustain traumatic brain injuries around twice as often as females.[9] The 20th century saw developments in diagnosis and treatment that decreased death rates and improved outcomes.
- ^ Jones DK (2010). Diffusion MRI. Oxford University Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-0-19-970870-3.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Rehman08was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c "TBI: Get the Facts". CDC. March 11, 2019. Retrieved May 28, 2019.
- ^ "Traumatic Brain Injury". medlineplus.gov. Retrieved May 28, 2019.
- ^ Silverberg ND, Iverson GL, ACRM Brain Injury Special Interest Group Mild TBI Task Force and the ACRM Mild TBI Definition Expert Consensus Group, ACRM Brain Injury Special Interest Group Mild TBI Task Force members, Cogan A, Dams-O'Connor K, Delmonico R, Graf MJ, Iaccarino MA, Kajankova M, Kamins J, McCulloch KL, McKinney G, Nagele D, Panenka WJ, Rabinowitz AR (May 19, 2023). "The American Congress of Rehabilitation Medicine Diagnostic Criteria for Mild Traumatic Brain Injury" (PDF). Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 104 (8): S0003–9993(23)00297–6. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2023.03.036. ISSN 1532-821X. PMID 37211140. S2CID 258821806.
- ^ "Basic Information about Traumatic Brain Injury | Concussion | Traumatic Brain Injury | CDC Injury Center". www.cdc.gov. March 6, 2019. Retrieved July 21, 2020.
- ^ "Prevention". CDC. March 4, 2019. Retrieved May 28, 2019.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Clark01was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
RaoLyketsoswas invoked but never defined (see the help page).