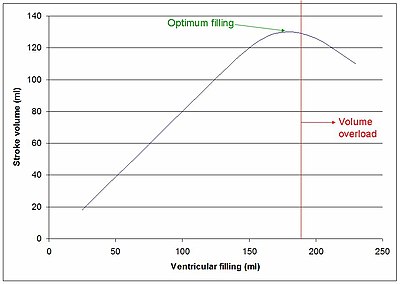
Volume overload refers to the state of one of the chambers of the heart in which too large a volume of blood exists within it for it to function efficiently. Ventricular volume overload is approximately equivalent to an excessively high preload. It is a cause of cardiac failure.[1]
- ^ Costanzo, Linda S. (2007). Physiology. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 81. ISBN 978-0-7817-7311-9.
