
Back الساحل الغربي للولايات المتحدة Arabic Западно крайбрежие на САЩ Bulgarian Costa Oest dels Estats Units Catalan Západní pobřeží Spojených států amerických Czech USA's vestkyst Danish Westküste der Vereinigten Staaten German Δυτική Ακτή των Ηνωμένων Πολιτειών Greek Okcidenta marbordo de Usono Esperanto Costa Oeste de los Estados Unidos Spanish Läänerannik (USA) Estonian
West Coast of the United States | |
|---|---|
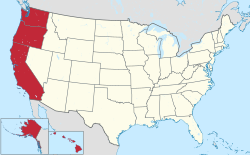 Location of the West Coast (red) as defined by the Census Bureau.in the United States (tan) | |
| Country | |
| Principal cities | Los Angeles San Diego San Jose San Francisco Sacramento Portland (Oregon) Seattle Anchorage Honolulu |
| Largest city | Los Angeles |
| Largest metropolitan area | Greater Los Angeles |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,009,688 sq mi (2,615,080 km2) |
| • Land | 895,287 sq mi (2,318,780 km2) |
| • Water | 21,433 sq mi (55,510 km2) |
| • Coastal | 28,913 sq mi (74,880 km2) |
| Highest elevation (Denali) | 20,310 ft (6,190.5 m) |
| Lowest elevation | −282 ft (−86 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 53,669,422[a] |
| Time zone | |
| Mountain | UTC−7:00 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−6:00 |
| Pacific | UTC−8:00 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−7:00 |
| Alaska | UTC−9:00 |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−8:00 |
| Hawaii | UTC−10:00 |
The West Coast of the United States, also known as the Pacific Coast and the Western Seaboard, is the coastline along which the Western United States meets the North Pacific Ocean. The term typically refers to the contiguous U.S. states of California, Oregon, and Washington, but it occasionally includes Alaska and Hawaii in bureaucratic usage. For example, the U.S. Census Bureau considers both states to be part of a larger U.S. geographic division.
- ^ "Highest and Lowest Elevations". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved April 29, 2021.
- ^ "Change in Resident Population of the 50 States, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico: 1910 to 2020" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 13, 2021.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).