
Back Wes-Germaanse tale Afrikaans Westgermanische Sprachen ALS የምዕራብ-ጀርመናዊ ቋንቋዎች ቤተሠብ Amharic Luengas chermanicas occidentals AN Westgermanisca spræca ANG لغات جرمانية غربية Arabic Llingües xermániques occidentales AST باتی ژرمن دیللری AZB Westgermanische Sprochn BAR Tataramon na Sulnopan na Alemaniko BCL
| West Germanic | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Originally between the Rhine, Alps, Elbe, and North Sea; today worldwide |
| Linguistic classification | Indo-European
|
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-5 | gmw |
| Linguasphere | 52-AB & 52-AC |
| Glottolog | west2793 |
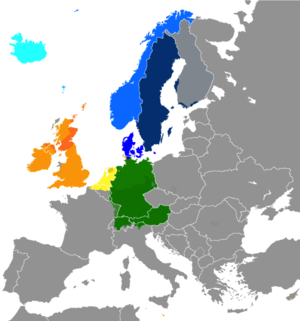 Extent of Germanic languages in present day Europe North Germanic languages West Germanic languages Dots indicate areas where multilingualism is common. | |
 Extent of Germanic languages in present day Africa
West Germanic languages | |
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into three branches: Ingvaeonic, which includes English, the Low German languages, and the Frisian languages; Istvaeonic, which encompasses Dutch and its close relatives; and Irminonic, which includes German and its close relatives and variants.
English is by far the most-spoken West Germanic language, with more than 1 billion speakers worldwide. Within Europe, the three most prevalent West Germanic languages are English, German, and Dutch. Frisian, spoken by about 450,000 people, constitutes a fourth distinct variety of West Germanic. The language family also includes Afrikaans, Yiddish, Low Saxon, Luxembourgish, Hunsrik, and Scots. Additionally, several creoles, patois, and pidgins are based on Dutch, English, or German.