
Back Röntgenabsorptionsspektroskopie German Espectroscopia de absorción de rayos X Spanish Spectrométrie d'absorption des rayons X French Spettroscopia XAS Italian X線吸収分光法 Japanese Absorpcja rentgenowska Polish Рентгенівська абсорбційна спектроскопія Ukrainian X射線吸收光譜 Chinese
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2021) |

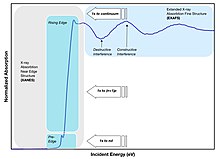
X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) is a widely used technique for determining the local geometric and/or electronic structure of matter.[1] The experiment is usually performed at synchrotron radiation facilities, which provide intense and tunable X-ray beams. Samples can be in the gas phase, solutions, or solids.[2]
- ^ "Introduction to X-Ray Absorption Fine Structure (XAFS)", X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials Sciences, Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, pp. 1–8, 2017-11-24, doi:10.1002/9781118676165.ch1, ISBN 978-1-118-67616-5, retrieved 2020-09-28
- ^ Yano J, Yachandra VK (2009-08-04). "X-ray absorption spectroscopy". Photosynthesis Research. 102 (2–3): 241–54. Bibcode:2009PhoRe.102..241Y. doi:10.1007/s11120-009-9473-8. PMC 2777224. PMID 19653117.