
Back Sigoot Afrikaans Zygote ALS Zigoto AN بويضة مخصبة Arabic Ziqot Azerbaijani Зігота Byelorussian Зыгота BE-X-OLD Зигота Bulgarian জাইগোট Bengali/Bangla Zigot BS
| Zygote | |
|---|---|
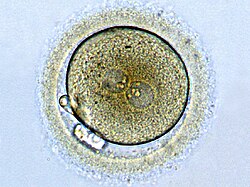 Zygote formation: egg cell after fertilization with a sperm. The male and female pronuclei are converging, but the genetic material is not yet united. | |
| Details | |
| Days | 0 |
| Precursor | Gametes |
| Gives rise to | Blastomeres |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D015053 |
| TE | E2.0.1.2.0.0.9 |
| FMA | 72395 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
| Part of a series on |
| Human growth and development |
|---|
 |
| Stages |
| Biological milestones |
| Development and psychology |
A zygote (/ˈzaɪˌɡoʊt/; from Ancient Greek ζυγωτός (zygōtós) 'joined, yoked', from ζυγοῦν (zygoun) 'to join, to yoke')[1] is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism. The sexual fusion of haploid cells is called karyogamy, the result of which is the formation of a diploid cell called the zygote or zygospore.
- ^ "English etymology of zygote". etymonline.com. Archived from the original on 2017-03-30.