
Back Arabiese syfers Afrikaans أرقام عربية Arabic Númberos arábigos AST Ərəb rəqəmləri Azerbaijani Ғәрәп цифрҙары Bashkir Арабскія лічбы Byelorussian Арабскія лічбы BE-X-OLD Арабски цифри Bulgarian আরবি সংখ্যা Bengali/Bangla Sifroù arabek Breton
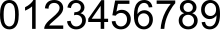
Arabiar zifrak —hindu zifrak,[1][2] hindu-arabiar zifrak[2][3] eta indo-arabiar zifrak[4] izenez ere ezagunak— zenbakizko hamar digituak dira (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9). Antzinako Indiako matematikariek garatu zuten hindu-arabiar zenbaki sistematik eratorriak dira;[5] sistema horretan, digituen sekuentzia bat (adibidez: 975) zenbaki bakartzat irakurtzen da. Tradizioak dio arabiar matematikariek eta persiar musulmanek indiar zifrak hartu zituztela Indian, eta mendebalderagoko arabiarrei pasatu zizkietela.
Europan Vigila izeneko kopista batek X. mendean Albeldako Kronika ezagunean erabili zituen, orduan Iruñeko Erresuman zegoen San Martin Albeldakoaren monasterioan.[6]
- ↑ Thorndike, Edward (2008): The Thorndike Arithmetics, Book One, BiblioBazaar, LLC, 102. orrialdea. ISBN 9780559242625
«1,2,3,4,5,6, etc., are called Arabic numerals or Hindu numerals.» - ↑ a b Schipp, Bernhard; Krämer, Walter (2008): Statistical Inference, Econometric Analysis and Matrix Algebra: Festschrift in Honour of Götz Trenkler, Springer, 387. orrialdea. ISBN 9783790821208
- ↑ Lumpkin, Beatrice; Strong, Dorothy (1995): Multicultural science and math connections: middle school projects and activities, Walch Publishing, 118. orrialdea. ISBN 9780825126598
- ↑ Fenna, Donald (2002): A Dictionary of Weights, Measures, and Units, Oxford University Press, New York, 90. eta 202. orrialdeak. ISBN 978-0198605225
«Fibonacci, in a book of 1202, brought the Indo-Arabic numerals, with their zero cypher and decimal point, into European culture.»
«... these characters are more appropriately called at least Indo-Arabic numerals.» - ↑ Bulliet, Richard; Crossley, Pamela; Headrick, Daniel; Hirsch, Steven; Johnson, Lyman (2010): The Earth and Its Peoples: A Global History, Volume 1, Cengage Learning, 192. orrialdea. ISBN 1439084742
«Indian mathematicians invented the concept of zero and developed the "Arabic" numerals and system of place-value notation used in most parts of the world today» - ↑ (Ingelesez) Bishko, Charles Julian. «Salvus of Albelda and Frontier Monasticism in Tenth-Century Navarre» Speculum 23 (4).