
Back قشرة مخية Arabic Corteya cerebral AST بئیین کورتکسی AZB Кара вялікіх паўшар’яў Byelorussian Мозъчна кора Bulgarian Moždana kora BS Escorça cerebral Catalan توێکڵی مێشک CKB Mozková kůra Czech Hjernebark Danish
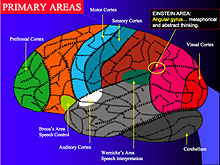
have different functions
The cerebral cortex is the most important part of the brain. In humans, it is by far the largest part of the brain.
Though this cannot be seen directly, different parts of the cortex have different functions (see diagram). It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness.
It is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain.[1] It has up to six layers of nerve cells. The human cerebral cortex is 2–4 mm (0.08–0.16 inches) thick.
In preserved brains, it is grey, so it is often called 'grey matter'. In contrast to gray matter that is formed from neurons and their unmyelinated fibers, the white matter below them is formed predominantly by myelinated axons interconnecting neurons in different regions of the cerebral cortex with each other and neurons in other parts of the central nervous system.
The surface of the cerebral cortex is folded in large mammals, such that more than two-thirds of it in the human brain is buried in the grooves.
- ↑ The cerebrum is the forebrain of vertebrates.