
Back Konveksie Afrikaans حمل (فيزياء) Arabic Conveición AST Konveksiya Azerbaijani Канвекцыя Byelorussian Конвекция Bulgarian Konvekcija BS Convecció Catalan Šíření tepla prouděním Czech Конвекци CV
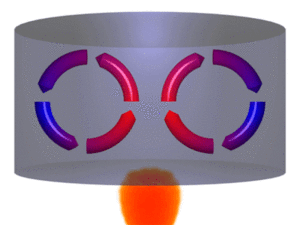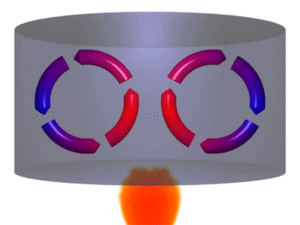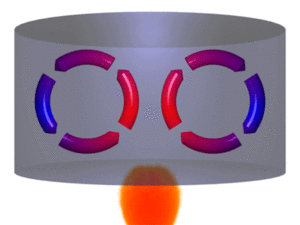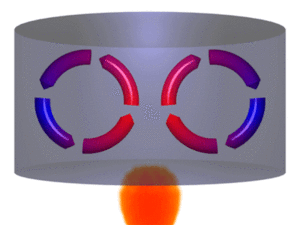
Convection is the movement of heat because of the movement of warm matter. Convection is defined as the method of heat transfer through a fluid from places of higher temperature to lower temperature by the movement of the molecules due to their different densities.
For example, atmospheric circulation moves warm air to cool places, causing wind. Wind, in turn, can enter and cool a room if the window is open. The movement of the clouds, the ocean currents and many types of heaters are examples of convection.