
Back Warm kol (geologie) Afrikaans Hot-Spot (Geologie) ALS نقطة ساخنة (جيولوجيا) Arabic Гореща точка Bulgarian Punt calent Catalan Horká skvrna Czech Hot spot (geologi) Danish Hotspot (Geologie) German Hotspot (geology) English Varma punkto Esperanto


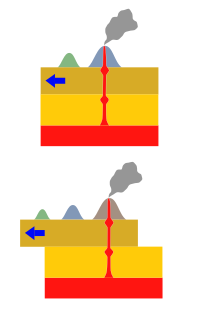
In geology, a hotspot or hot spot is a portion of the Earth's surface which is volcanic. This may be caused by a rising mantle plume or some other cause.[2] Hotspots may be far from tectonic plate boundaries.
A volcanic hotspot is where magma pushes up from deep in the Earth's crust or mantle, and creates a volcano. The Earth's plates may move along, creating a new volcano above the hotspot while moving the older volcanoes away. This creates a chain of islands, such as in Hawaii.
- ↑ Courtillot V. et al 2003. Three distinct types of hotspots in the Earth's mantle (2003). "Three distinct types of hotspots in the Earth's mantle". Earth Sci. Planet. Lett. 205 (3–4): 295–308. Bibcode:2003E&PSL.205..295C. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(02)01048-8.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ↑ "Do plumes exist?". Archived from the original on 2011-01-19. Retrieved 2010-04-25.