
Back Liter Afrikaans Liter ALS Litro AN لتر Arabic إيطرو ARY ليتر ARZ লিটাৰ Assamese Llitru AST Litr Azerbaijani لیتر AZB
| Litre | |
|---|---|
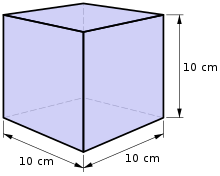 One litre is the volume of a cube with 10 cm sides | |
| General information | |
| Unit system | Non-SI unit accepted for use with SI |
| Unit of | Volume |
| Symbol | l[1] or L[1] |
| In SI base units: | 1 l = 10−3 m3 |
A litre (international spelling) or liter (American spelling) is one of the metric units of volume. It is not a basic SI unit, but it is a supplementary unit.
One litre is the volume of 1000 cubic centimetres, that is a cube of 10 × 10 × 10 centimetres (1000 cm3). One litre of water at 4 °C (277 K; 39 °F) has the mass of exactly one kilogram. This results from the definition given in 1795, where the gram was defined as the weight of one cubic centimetre of melting ice.[2]
Liters are usually utilized to measure the volume of liquids, this is because the density of liquids can vary a lot. However it can be applied to solids as well, for example 1 liter of Iron is around 7.7 kg. The symbol for litre is l or L.[1] The script letter ℓ is also sometimes used.
For smaller volumes, the decilitre is used: 10 decilitres = one litre.
For smaller volumes, the centilitre is used: 100 centilitres = one litre.
For smaller volumes, the millilitre is used: 1000 millilitres = one litre.
The capital letter "L" is preferred by some people as the small "l" can look like the number one "1".
- 1 litre = 0.2200 imperial gallons
- 1 litre = 0.2642 US gallons
- 1 imperial gallon = 4.5461 litres
- 1 US gallon = 3.7854 litres
- 1 litre = 1 dm3
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 International Bureau of Weights and Measures (2006), The International System of Units (SI) (PDF) (8th ed.), p. 124, ISBN 92-822-2213-6
- ↑
"Decree on weights and measures". 7 April 1795.
Gramme, le poids absolu d'un volume d'eau pure égal au cube de la centième partie du mètre, et à la température de la glace fondante.
English translation: "Gramme: the absolute weight of a volume of pure water equal to the cube of the hundredth part of the meter, at the temperature of melting ice."