Back عدد سالب Arabic Númberu negativu AST Mənfi ədədlər Azerbaijani Адмоўны лік Byelorussian Адмоўны лік BE-X-OLD ঋণাত্মক ও অঋণাত্মক সংখ্যা Bengali/Bangla Niver leiel Breton Negativan broj BS Һөөргэ тоо BXR Nombre negatiu Catalan
A negative number, also known as a minus number or below number, is an opposite number that is smaller than zero. For example:
- If a positive number is distance up, then a negative number is distance down.
- If a positive number is distance to the right, then a negative number is distance to the left.
- If a positive number is a deposit to a bank account, then a negative number is a withdrawal from that bank account.
- If a positive number is a quantity of minutes in the future, then a negative number is a quantity of minutes in the past.
- If a positive number means addition, then a negative number means subtraction.
The counting numbers (1, 2, 3, and so on) are all positive numbers. The positive numbers, negative numbers, and the number zero, taken together, are called "signed numbers" or integers.
The number zero is neither positive nor negative. Zero is its own opposite; so +0 = −0. That is, zero steps to the right is the same as zero steps to the left.
A negative number is always less than zero.
A negative number is written by putting a minus sign, "−", in front of a positive number. For example, 3 is a positive number, but −3 is a negative number. It is read "negative three" or "minus three"; it means the opposite of 3.
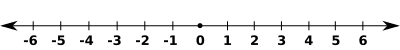
Negative numbers are left of zero on a number line. A number and its opposite are always the same distance from zero. The negative number −3 is just as far to the left of zero as 3 is to the right of zero:
Sometimes, for emphasis, we write the pair of opposite numbers as −3 and +3.
A number and its opposite always add to zero. So the sum of −3 and +3 is 0. We can write this either as −3 + 3 = 0 or as 3 + (− 3) = 0. In addition, a number and its opposite are said to "cancel each other out".
The set of negative real numbers is sometimes written as .[1]
- ↑ "Comprehensive List of Algebra Symbols". Math Vault. 2020-03-25. Retrieved 2020-10-12.