
Back Bahsa Occitan ACE Окситаныбзэ ADY Oksitaans Afrikaans Okzitanische Sprache ALS ኦክሲታንኛ Amharic Idioma occitán AN اللغة الأكستانية Arabic لغه قسطانيه ARZ Idioma occitanu AST Oksitan dili Azerbaijani
| Occitan | |
|---|---|
| occitan, lenga d'òc, provençal | |
| Native to | France, Spain, Italy, Monaco |
Native speakers | estimates range from 100,000 to 800,000 (2007–2012)[1][2] |
Early form | |
| Dialects |
|
| Official status | |
Official language in | Catalonia (Spain) |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Regulated by | Conselh de la Lenga Occitana;[4] Congrès Permanent de la Lenga Occitana;[5] Institut d'Estudis Aranesi[6] |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | oc |
| ISO 639-2 | oci |
| ISO 639-3 | oci – inclusive codeIndividual code: sdt – (Judeo-Occitan) |
| Glottolog | occi1239 |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-g & 51-AAA-f |
 | |
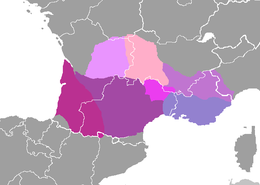 various dialects of Occitan | |
Occitan[7][8] is known as lenga d'òc by its native speakers.
It is a Romance language spoken in the south of France, the Occitan Valleys of Italy, the Val d'Aran of Catalonia and Monaco. The regions together called Occitania. Of course, this is an unofficial name for a region in three countries! Its justification is that it is united by a culture.
Occitan took a different path from Latin to the main official languages. It is sometimes called lenga d'òc ("language of oc", French: langue d'oc) because its word for yes is òc, as opposed to oil (oui) or sì in other languages. That is one way to classify Romance languages.
Occitan is an official language of Catalonia.[9] Since September 2010, the Parliament of Catalonia has considered Aranese Occitan to be the officially preferred language for use in the Val d'Aran.
- ↑ Fabrice BERNISSAN (2012). "Combien l'occitan compte de locuteurs en 2012 ?", Revue de Linguistique Romane, 76 (12/2011-07/2012), pp. 467-512
- ↑ « De fait, le nombre des locuteurs de l’occitan a pu être estimé par l’INED dans un premier temps à 526 000 personnes, puis à 789 000, » ("In fact, the number of occitan speakers was estimated by the French Demographics Institute at 526,000 people, then 789,000") Philippe Martel, "Qui parle occitan ?" in Langues et cité n°10, December 2007.
- ↑ Norme in materia di tutela delle minoranze linguistiche storiche, Italian parliament
- ↑ CLO's statements in Lingüistica Occitana (online review of Occitan linguistics).[permanent dead link]
- ↑ "Page d'accueil". Région Nouvelle-Aquitaine - Aquitaine Limousin Poitou-Charentes. Archived from the original on 2012-01-27. Retrieved 2013-02-20.
- ↑ "Reconeishença der Institut d'Estudis Aranesi coma academia e autoritat lingüistica der occitan, aranés en Aran - Conselh Generau d'Aran". www.conselharan.org.
- ↑ Oxford Advanced Learner's Dictionary, 7th edition, 2005.
- ↑ Regional pronunciations: occitan = [u(t)siˈtaⁿ, u(t)siˈtɔ, ukʃiˈtɔ].
- ↑ As stated in its Statute of Autonomy approved. See Article 6.5 in the Parlament-cat.net Archived 26 August 2013 at the Wayback Machine, text of the 2006 Statute of Catalonia (PDF)