Back بيريميدين Arabic پیریومیدین AZB Пірымідзін Byelorussian Пиримидин Bulgarian Pirimidin BS Pirimidina Catalan پیریمیدین CKB Pyrimidin Czech Pyrimidin Danish Pyrimidin German
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Pyrimidine
| |||
| Other names
1,3-Diazine, m-Diazine
| |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
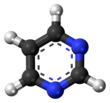
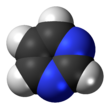
Pyrimidines include three of the bases in DNA and RNA.
A pyrimidine is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound, similar to purine.[1] It has nitrogens at positions 1 and 3 in the ring.[2][3]
- ↑ Gilchrist T.L. (1997). Heterocyclic chemistry. New York: Longman. ISBN 0-582-27843-0.
- ↑ Joule, John A.; Mills, Keith, eds. (2010). Heterocyclic chemistry (5th ed.). Oxford: Wiley. p. 250. ISBN 978-1-405-13300-5.
- ↑ Brown H.C. et al 1955. In Baude, E.A. and Nachod, F.C., Determination of organic structures by physical methods. Academic Press, New York.