
Back Qing-dinastie Afrikaans Qing-Dynastie ALS Улу Чиҥ каандык ALT የጪንግ ሥርወ መንግሥት Amharic Dinastía Qing AN किंग वंश ANP سلالة تشينغ الحاكمة Arabic Dinastía Qing AST Tzin sülaləsi Azerbaijani چینق سولالهسی AZB
Qing Dynasty 清朝 | |
|---|---|
| 1636–1912 | |
| Anthem: 鞏金甌 Gǒng Jīn'ōu "Cup of Solid Gold" (1911–1912) | |
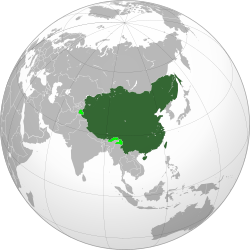 The Qing dynasty at its greatest extent in 1760 superimposed on a modern world map. Territory under its control shown in dark green; territory claimed but not under its control shown in light green. | |
| Capital | Mukden (1636–1644) Beijing (1644–1912) |
| Official languages | Manchu, Mandarin Chinese |
| Religion | Chinese Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Tibetan Buddhism, Chinese folk religion |
| Demonym(s) | Chinese |
| Government | Absolute monarchy[a] |
| Emperor | |
• 1636–1643 (founder) | Chongde Emperor |
• 1643–1661 (first in Beijing) | Shunzhi Emperor |
• 1908–1912 (last) | Xuantong Emperor |
| Regent | |
• 1643–1650 | Dorgon, Prince Rui |
• 1908–1911 | Zaifeng, Prince Chun |
| Prime Minister | |
• 1911 | Yikuang, Prince Qing |
• 1911–1912 | Yuan Shikai |
| Area | |
• Total | 13.400000 km2 (5.173769 sq mi) |
| Today part of | People's Republic of China, Mongolia |

The Qing Dynasty or the Qing Empire (Chinese: 清朝; pinyin: Qīng cháo) was a dynasty of rulers of China from 1644 to 1912. The dynasty was founded by the Manchus and so its other name is the Manchu dynasty. The surname of the Qing emperors was Aisin Gioro. It became the Republic of China in 1912 after the 1911 Xinhai Revolution.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).

